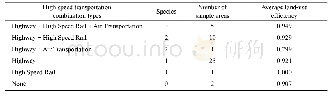
《Table 7 Statistics of soil bulk density in different land use types in Chengdu Plain》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Spatial variability of soil bulk density and its controlling factors in an agricultural intensive area of Chengdu Plain,Southwest China"》
Different capital letters in column are significantly different among land use types in each layer at P<0.05;different lowercase letters in row are significantly different among soil layers at P<0.05.
Although analysis above has evaluated the relative contribution of structural or random factors on the spatial variability of soil bulk density,more efforts are needed to identify which one of the structural or random factors is the dominated factor in each soil layer.In our study,soil elevation,parent material and soil types including soil group,subgroup and soil genus were characterized as structural factors while soil organic matter and land use were classified as random factors.According to the stepwise regression analysis(Table 8),we found soil organic matter was determined as the controlling factor on the spatial variability of soil bulk density in each layer(Table 8).Numerous researches have shown soil organic matter was significantly negatively related with soil bulk density(Deng et al.2014;Wang et al.2014;Yang et al.2016).In agreement with the previous researches,our study also found soil bulk density in the study area played significantly negative relationship with soil organic matter in each soil layer(Table 4).Moreover,the correlation coefficient r decreased with increasing soil layer,indicating the effects of soil organic matter on bulk density became weaker as soil layer increasing.It is mainly because soil organic matter decreases with increasing soil layer due to the reduced exogenous input of organic material such as litter,roots and animal debris.
| 图表编号 | XD0047430700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.20 |
| 作者 | LI Shan、LI Qi-quan、WANG Chang-quan、LI Bing、GAO Xue-song、LI Yi-ding、WU De-yong |
| 绘制单位 | College of Resources, Sichuan Agricultural University、College of Resources, Sichuan Agricultural University、College of Resources, Sichuan Agricultural University、College of Resources, Sichuan Agricultural University、College of Resources, Sichuan Agricultu |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 7 Statistics of soil bulk density in different land use types in Chengdu Plain”的人还看了
-

- 表9 不同土地利用类型各适宜性等级所占面积统计表Table 9 The area statistics of the different land use types of suitability levels单位 (hm2)
-
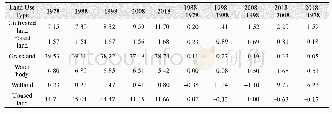
- Table 5 Area ratios and change rates of different land use types in Yarkant River basin(1978–2018)(%)
-
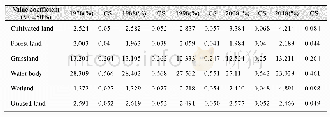
- Table 7 Sensitivity coefficient change of ESV for different land use types in 1978,1988,1998,2008,and2018 in Yarkant Riv
-
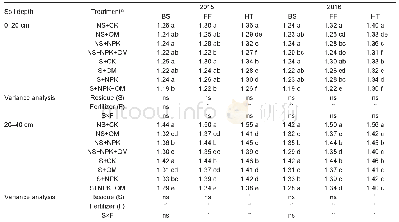
- Table 4 Soil bulk density (BD, g cm–3) under different residue management and fertilizer treatments in 2015 and 20161)