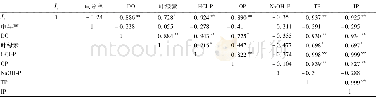
《Table 2.Pearson correlation coefficient between the respiration rate and water parameters.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Effects of Rice-Fish Co-culture on Oxygen Consumption in Intensive Aquaculture Pond》
TSS,Total suspended solid;COD,Chemical oxygen demand;TN,Total nitrogen;TP,Total phosphorous;DIP,Dissolved inorganic phosphorous.*indicate significant correlation at the 0.05 level.
The changes of water parameters revealed that rice-fish co-culture in aquaculture pond improved the water quality(Table 1).Rice-fish co-culture significantly reduces the water temperature of aquaculture pond,reducing damage to fish by high temperature(such as higher metabolism,respiration and oxygen demand of fish,and lower solubility of dissolved oxygen and more toxic substances in water)in intensive aquaculture ponds during the summer(Siikavuopio et al,2012).The cooling effect of rice was primarily attributed to the shading of rice leaves in the co-culture pond.CODwas reduced by 44.6%and 6.5%by rice cultivation in the catfish and shrimp ponds,respectively(Table 1).The removal efficiency of this new rice-fish co-culture system on COD is comparable with the aquaponics systems,in which vegetable and triticeae crops are used to restore aquaculture wastewater(Snow et al,2008).Rice cultivation also significantly reduced eutrophication in the pond water particularly in the yellow catfish pond.The contents of TN,TP and Kwere reduced by 50.2%,59.6%and 40.4%through rice cultivation in the yellow catfish pond,respectively.The restoration efficiency was lower than that of the aquaponics systems(Ghaly et al,2005;Snow et al,2008;Graber and Junge,2009).This was most likelydue to the cultivation density of rice in the fish pond being lower than that of vegetable and triticeae crops in the aquaponics systems.
| 图表编号 | XD0040097100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.28 |
| 作者 | LI Fengbo、SUN Zhiping、QI Hangying、ZHOU Xiyue、XU Chunchun、WU Dianxin、FANG Fuping、FENG Jinfei、ZHANG Ning |
| 绘制单位 | China National Rice Research Institute、Integrated and Urban Plant Pathology Laboratory, University of Liège、College of Agriculture and Biotechnology, Zhejiang University、Agricultural Extension Center of Zhuji City、China National Rice Research Institute、Ch |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2.Pearson correlation coefficient between the respiration rate and water parameters.”的人还看了
-

- Table 5 Correlation coefficients between the cold injury index of bitter gourd and main agronomic traits of bitter gourd
-
- Table 6 The correlation coefficient values between temperature extremes in CA and atmospheric circulations
-
- Table 7 The correlation coefficient values between precipitation extremes in CA and atmospheric circulations
-

- Table 1.Correlation coefficients between the PCs and moisture incomes across the four boundaries of Northeast China duri