《Table 1Summary of measures taken to restore Lake Taihu since 2007.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Why Lake Taihu continues to be plagued with cyanobacterial blooms through 10 years(2007–2017) efforts》
With the expansion of urban,industry,and agriculture after World War II,eutrophication firstly emerged as a major water quality threat in small water bodies[1].As the increasing magnitudes and scales of nutrient pollution and habitat alteration,many of the world’s large lakes exhibit symptoms of eutrophication,e.g.,toxic cyanobacterial blooms,deoxygenation,and habitat loss.These symptoms were noted in shallow large lakes such as Okeechobee and Winnebago(USA),Winnipeg(Canada),Peipsi(Estonia),Balaton(Hungry),Chaohu and Taihu(China),Kasumigaura(Japan);in shallow parts of large lakes including Lakes Champlain,Ontario,and Erie(Canada/USA),Huron(USA),Maracaibo(Venezuela),Victoria(Africa);and in segments of immense water bodies such as Tanganyika(Africa)(Table S1 online) .These large aquatic ecosystems pose a tremendous challenge from mitigation and restoration perspectives.
| 图表编号 | XD0036051800 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.30 |
| 作者 | Boqiang Qin、Hans W.Paerl、Justin D.Brookes、Jianguo Liu、Erik Jeppesen、Guangwei Zhu、Yunlin Zhang、Hai Xu、Kun Shi、Jianming Deng |
| 绘制单位 | State Key Laboratory for Lake Science and Environment, Nanjing Institute of Geography & Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences、The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Institute of Marine Sciences、College of Environment, Hohai University、Water Res |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1Summary of measures taken to restore Lake Taihu since 2007.”的人还看了
-
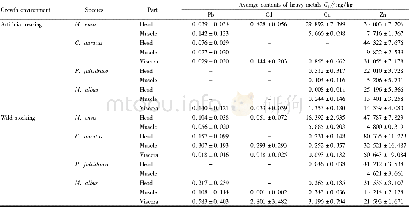
- Table 2 Average contents of heavy metals in different parts of aquatic products from Lake Taihu (±s, n=24)