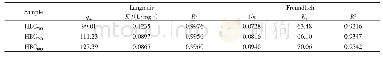
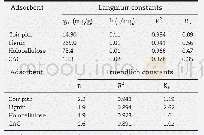
《Table 4–Parameters fitted by Langmuir and Freundlich models.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《One-step preparation of polyimide-inlaid amine-rich porous organic block copolymer for efficient removal of chlorophenols from aqueous solution》
River water contains various inorganic and organic pollutants such as heavy metal ions,dyes,phenols,etc.In the natural adsorption process of a target contaminant,these pollutants compete with the adsorbate,which may reduce the adsorption capacity(Fukuhara et al.,2006;Nam et al.,2014).The capacities of 2,4-DCP adsorption by ARPOP and PI-b-ARPOP in river water are plotted in Fig.10a,and the linear fitting curves and parameters of the Langmuir model are shown in Fig.10b.Compared with the results of adsorption experiments in ultra-pure water(Fig.8 and Table 4),the adsorption amounts in river water were slightly lowered.In detail,the qmaxvalues for MA/TA(4/4),MA/TA/PMDA(4/3/1),MA/TA/PMDA(4/2/2)and MA/TA/PMDA(4/1/3)decreased from 188.70 mg/g240.96 mg/g,282.49 mg/g and 220.26 mg/g to 185.19 mg/g234.74 mg/g,277.78 mg/g and 213.68 mg/g,respectively.This implied that the micropollutants in river water partly competed with 2,4-DCP in the adsorption process.Hence the results show that PI-b-ARPOP can be successfully applied in the practical treatment of chlorophenols in natural wastewater.
| 图表编号 | XD0033526000 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.04.15 |
| 作者 | Yanyang Liu、Haijian Ou、Shangqing Li、Qingliang You、Huixian Liu、Guiying Liao、Dongsheng Wang |
| 绘制单位 | Engineering Research Center of Nano-Geomaterials of Ministry of Education,Faculty of Material Science and Chemistry,China University of Geosciences、Engineering Research Center of Nano-Geomaterials of Ministry of Education,Faculty of Material Science and C |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4–Parameters fitted by Langmuir and Freundlich models.”的人还看了
-
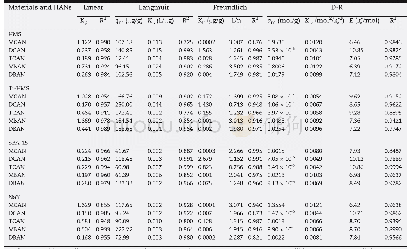
- Table 4–Isotherm parameters derived from the Linear, Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin and Radushkevich (D-R) models for
-
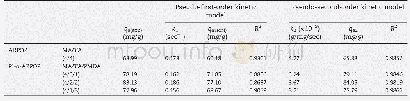
- Table 2–Parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich fits for As (V) adsorption on Zn0.6Fe2.4O4, α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe3O4.
-
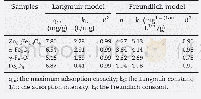
- Table 3–Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherm for TMA adsorption by coir pith, lignin and holocellulose extracted