《Table 1 Studies design》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Image-guided lens extraction surgery: a systematic review》
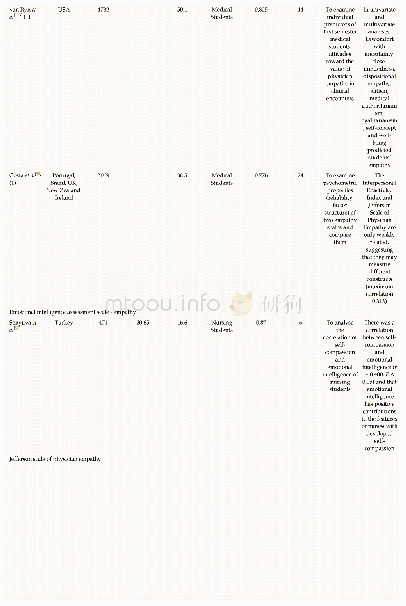
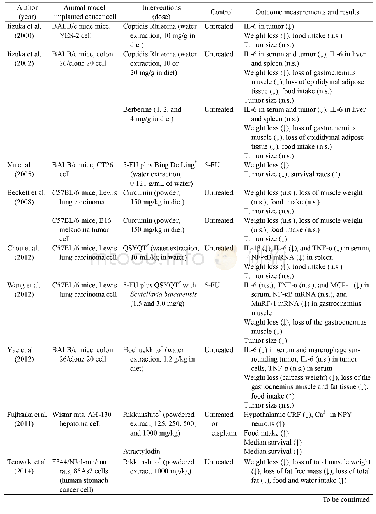
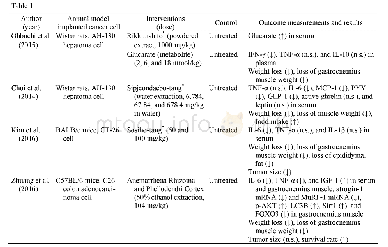
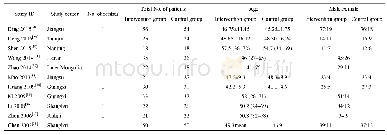
Studies’Design The present review included 1 descriptive[25]and 20 comparative[1-2,22,24,26-41]studies.Among them,12 were prospective studies[1-2,25-33,41]and 7 retrospective[22,24,34-38],while there was not any relative statement in the rest 2studies[39-40](Table 1).Eight studies compared the accuracy of toric IOL alignment using image-guided systems versus different conventional manual marking techniques[24-28,34,39,41],whereas Hura and Osher[22]made a comparative evaluation of the alignment meridian generated by two different imageguided systems.Among the other objectives of Mayer et al study[28]was the comparison of the required time of cataract surgery with implantation of a toric IOL using digital and manual marking techniques,while the main objective in the study of Thomas et al[29]was the comparison of the duration of the preoperative examination and patient comfort between measurements with an image-guided system and other established keratometry devices.In addition,7studies[1-2,30,35-37,40]made a comparison in the keratometric measurements of image-guided systems with other devices used in current clinical practice,while two studies[31,37]compared an image-guided system with other devices regarding the IOL power calculation.Finally,the intraobserver repeatability[1,30,32-33,36,40],the reproducibility[32,36],and the interchangeability[1-2,33,36]of keratometric measurements obtained with image-guided systems were analyzed in some studies of this review.
| 图表编号 | XD0032750500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.18 |
| 作者 | Eirini-Kanella Panagiotopoulou、Panagiota Ntonti、Maria Gkika、Aristeidis Konstantinidis、Irfan Perente、Doukas Dardabounis、Konstantinos Ioannakis、Georgios Labiris |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Ophthalmology,University Hospital of Alexandroupolis、Department of Ophthalmology,University Hospital of Alexandroupolis、Department of Ophthalmology,University Hospital of Alexandroupolis、Department of Ophthalmology,University Hospital of Ale |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |