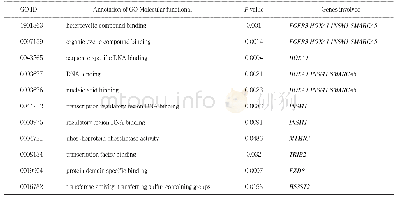
《Table 2–Classification of KASP markers with known functional annotation/domain used in this study.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Development of P genome-specific SNPs and their application in tracing Agropyron cristatum introgressions in common wheat》
The polymorphisms of the 230 selected SNPs were first tested using KASP genotyping assays between A.cristatum Z559 and common wheat cv.Fukuhokomugi.To examine the genome specificity of the SNPs and eliminate the false positives,markers polymorphic between Fukuhokomugi and A.cristatum were further screened in 17 additional wheat genetic backgrounds.In the KASP genotyping assays,target SNPs that presented three obvious clusters and showed allele 1 in wheat varieties,allele 2 in A.cristatum Z559,and heterozygosity(allele 1/allele 2)in the mixed samples of Z559 and Fukuhokomugi were therefore specific to A.cristatum and could be used for P genome detection.Seventy of the 230 SNPs were polymorphic between Fukuhokomugi(allele 1)and A.cristatum(allele 2)and had heterozygous alleles(allele 1/allele2)in the mixed samples of Z559 and Fukuhokomugi(Fig.2-A).These 70 SNPs,accounting for 29.6%of the total markers genotyped,were possibly specific to the P genome(Table 2).However,two of them were detected in other wheat varieties and were thus false positives.Consequently,these 68 P genome-specific SNPs(Table S3)were used to identify A.cristatum P chromatin in multiple wheat backgrounds.
| 图表编号 | XD0029304200 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.04.01 |
| 作者 | Huihui Ma、Jinpeng Zhang、Jing Zhang、Shenghui Zhou、Haiming Han、Weihua Liu、Xinming Yang、Xiuquan Li、Lihui Li |
| 绘制单位 | Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences、Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences、Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences、Institute of Crop Sciences, Chinese Academy of A |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2–Classification of KASP markers with known functional annotation/domain used in this study.”的人还看了
-
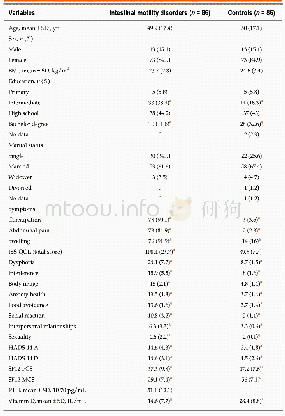
- Table 1 Characteristics of patients with functional chronic constipation with intestinal motility disorders and of contr