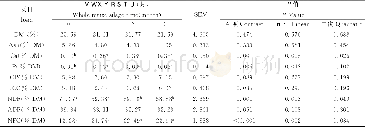
《Table 1 Effect of inoculation on N content of plant in insoluble P soil》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Effect of Inoculation Rhizobium and Response of Soybean-Rhizobium System to Insoluble Phosphate》
Al-P,Fe-P replace of aluminium phosphate and iron phosphate,respectively.*indicates significant difference against CK at 5%level students'F-test.No significant difference against CK at 1%level students'F-test.The same as below.
Phosphorus appeared essential for both nodulation and N2 fixation.Phosphorus was required by soybean for growth and promoted N uptake.Inoculation with Rhizobium strains affected higher root phosphorus content in Fe-P soil than Al-P soil,but some strains did not increase phosphorus content of root compared to other inoculants.Inoculation with C46 had the highest P content of plant in Al-P soil,increasing 31.6%when compared with CK U110 in Table 2.On the average,inoculation with Rhizobium strains increased higher phosphorus content of plant in Al-P soil than Fe-P soil in Tables 3-4.However,only inoculation with CW54significantly enhanced phosphorus uptake of plant in Al-P and Fe-P soil as compared with other inoculants,whereas in Fe-P soil more higher than in Al-P soil,increasing 96.2%(Fe-P)and 8.2%(Al-P),when compared with CK U110 in Table 2,respectively.
| 图表编号 | XD0014150100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.03.25 |
| 作者 | Li Xiu-ping、Chen Shu-zhen、Zhang Yan-lai、Cheng Yan-bo、Nian Hai |
| 绘制单位 | Guangdong AIB Polytechnic College、National Center for Soybean Improvement, College of Agriculture, South China Agriculture University、National Center for Soybean Improvement, College of Agriculture, South China Agriculture University、Guangdong AIB Polytec |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1 Effect of inoculation on N content of plant in insoluble P soil”的人还看了
-
- 表2 青贮时间对全株玉米常规营养成分含量的影响Table 2 Effect of silage time on the content of conventional nutrient in whole maize





