《Table 1 Literature review of comparative trials on oral feeding after esophagectomy》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Optimal timing and route of nutritional support after esophagectomy: A review of the literature》
Studies that have focused on EOF after esophagectomy alone have largely confirmed that there is a significant benefit with regards to return of bowel function and hospital stay.A prospective cohort study from Sun et al[22]in 2015 comparing EOF(POD1)to late feeding(POD7)after minimally-invasive McKeown esophagectomy confirmed that EOF patients had shorter ROBF and improved short-term quality of life metrics without any meaningful increase in complications.Like Mahmoodzadeh and Lassen,their EOF group was not supplemented with supplemental artificial enteral nutrition.In the long term,patients that started EOF had similar changes in weight after one year and required fewer procedural interventions related to nutrition(i.e.,prolonged tube feeding,restarting tube feeding,placement of a catheter for TPN)than patients with delayed oral feeding[23].Additionally,early oral feeding after esophagectomy also decreases the stress response after minimally-invasive McKeown esophagectomy as measured by levels of circulating inflammatory cytokines[24].
| 图表编号 | XD0087251900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.08.21 |
| 作者 | Richard Zheng、Courtney L Devin、Michael J Pucci、Adam C Berger、Ernest L Rosato、Francesco Palazzo |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Surgery, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital.Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia University and Thomas Jefferson University、Department of Surgery, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital.Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia Univ |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1 Literature review of comparative trials on oral feeding after esophagectomy”的人还看了
-
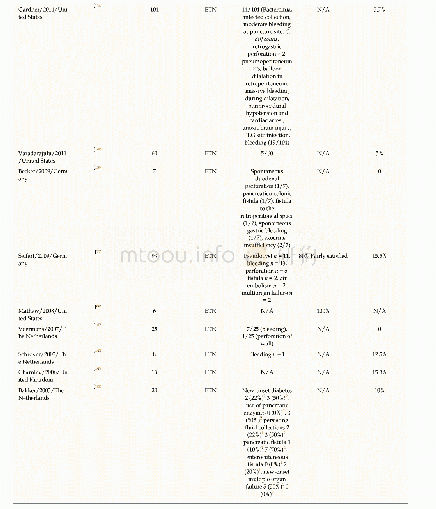
- Table 2 Peer-reviewed literature reports on the clinical outcomes of patients undergoing endoscopic transluminal necrose
-
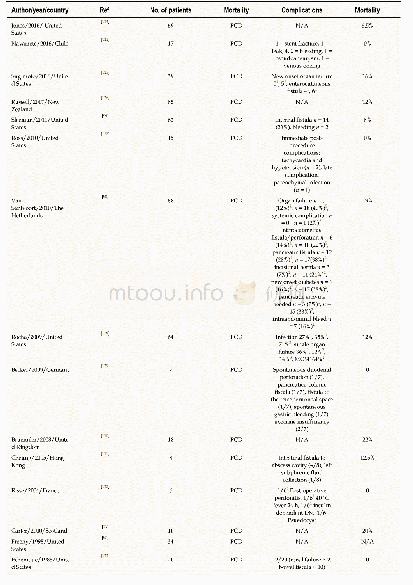
- Table 1 Peer-reviewed literature reports on the clinical outcomes of patients undergoing percutaneous catheter drainage
-
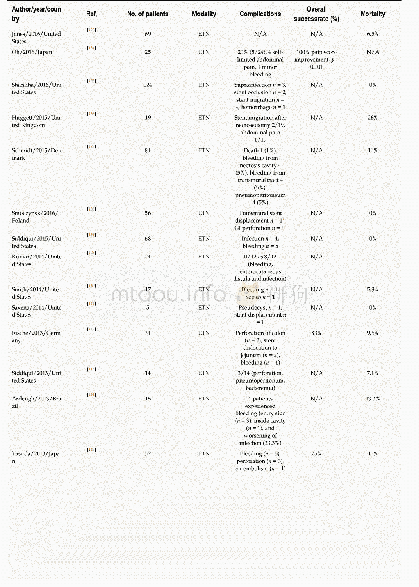
- Table 2 Peer-reviewed literature reports on the clinical outcomes of patients undergoing endoscopic transluminal necrose





