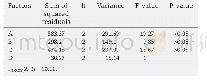
《Table 1 Results of X-ray point-wise microanalysis of Nimonic 80A-alloy after laser alloying with bo
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《添加铌和钼对Nimonic 80A合金激光硼化表面显微组织和磨损行为的影响(英文)》
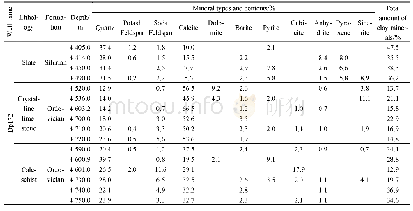
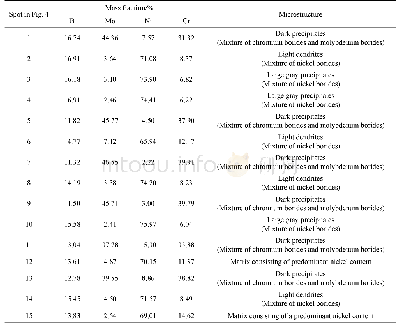
The SEM images of Nimonic 80A-alloy,laseralloyed with boron and molybdenum,were shown in Fig.4.In order to examine the microstructure in details,the SEM images were taken from different areas of the re-melted zone.Simultaneously,the contents of the main elements(nickel,chromium,molybdenum and boron)were measured in 15 different areas of laser-alloyed layer using EDS method.The results of point-wise X-ray microanalysis were specified in Table 1.The four characteristic components of microstructure were clearly visible in the re-melted zone:dark precipitates(marked as 1,5,7,9,11 and 13 in Fig.4),large gray precipitates(marked as 3,4 and 10 in Fig.4),light dendrites(marked as 2,6,8 and 14 in Fig.4)and matrix(marked as 12 and15 in Fig.4).EDS results from the dark precipitates showed the increased chromium and molybdenum contents as well as the relatively low nickel content.This indicated the occurrence of the mixture of chromium borides(Cr2B)and molybdenum borides(Mo2B,Mo2B5and MoB)in these areas.It should be noticed that chromium and molybdenum borides appeared in the microstructure together.This dependence confirmed the results of detailed X-ray line microanalysis,presented in Fig.2(b).It also indicated the possibility of formation of complex(Cr,Mo)x By borides.The light dendrites as well as the large gray precipitates were characterized by high nickel content;whereas the contents of chromium and molybdenum decreased in this area.These dendrites and precipitates occurred across the whole re-melted zone regardless of the distance from the surface.The predominant percentage of a mixture of nickel borides(Ni2B,NiB,Ni3B and Ni4B3)was most probable in these areas.In the matrix area,the contents of nickel and chromium were similar to those of base material.The increased content of boron could result from X-ray emission from the adjacent areas.The EDS detector also measured radiation energy from other phases.The matrix was also alloyed with molybdenum as a consequence of the treatment used.
| 图表编号 | XD0064472500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.01 |
| 作者 | N.MAKUCH、P.DZIARSKI、M.KULKA、A.PIASECKI、M.TULISKI、R.MAJCHROWSKI |
| 绘制单位 | Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, Poznan University of Technology、Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, Poznan University of Technology、Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, Poznan University of Technology、Institute of Ma |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |