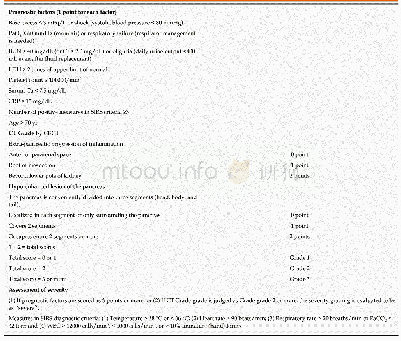
《Table 1 Differential diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Cyst fluid glucose: An alternative to carcinoembryonic antigen for pancreatic mucinous cysts》
IPMN:Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm;MCN:Mucinous cystic neoplasm;PC:Pseudocyst;SCN:Serous cystic neoplasm;NET:Neuroendocrine tumor;SPN:Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm;MPD:Main pancreatic duct;CEA:Carcinoembryonic antigen.
The accurate diagnosis of PCLs is critical to guarantee the best management for these patients,whether through surgical resection or periodic surveillance[6-8].Unfortunately,there is no a single test accurate enough to assure a definitive diagnosis for all PCLs,particularly for those that are isolated unilocular cystic lesions,with neither perceptible communication with the main pancreatic duct(MPD)nor previous episodes of pancreatitis[9].Therefore,a combination of information obtained from demographics,clinical history and imaging,as well as cytopathology and cyst fluid markers obtained by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration(EUS-FNA),has been used for the differential diagnosis of PCLs(Table 1).
| 图表编号 | XD0064283500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.05.21 |
| 作者 | César Vivian Lopes |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Gastroenterology and Digestive Endoscopy, Santa Casa Hospital |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |