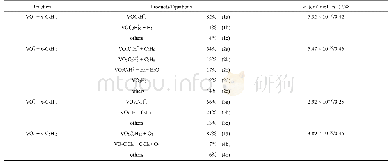
《Table 1–Reaction rate constants for isoprene, MVK and MACR (cm3/ (molecule.sec)》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Sources of methacrolein and methyl vinyl ketone and their contributions to methylglyoxal and formaldehyde at a receptor site in Pearl River Delta》
aCarter and Atkinson,1996bApel et al.,2002.
The evolution of isoprene and its oxidation products in the atmosphere is different from that determined in the laboratory studies due to continuous emissions of isoprene,radical variations,and anthropogenic emissions of MACR and MVK in the atmosphere(Karl et al.,2009).Therefore,to advance the understanding of the behaviors of isoprene and its oxidation products in the real ambient air,many field studies have been conducted to investigate the evolution of isoprene and its contributions to O3formation in different environments(e.g.,Jones et al.,2011;Park et al.,2011;Roberts et al.,2006;Spaulding et al.,2003).The most frequently used method for studying the contributions of secondary formation to the observed MACR and MVK concentrations is based on the ratios of isoprene and its oxidation products,i.e.,[MACR]/[MVK],[MACR+MVK]/[isoprene],[MVK]/[isoprene]and[MACR]/[isoprene].This method relies on differences in the photochemical reactivities of isoprene and its oxidation products in the atmosphere(Table 1).However,ratio methods are based on the assumption that no fresh emissions of isoprene,MACR and MVK are introduced into the atmosphere or,alternately,isoprene emissions are constant during the processes and physical processes do not influence the observed ratios of isoprene and its oxidation products during transport.Therefore,any other emissions of MACR and MVK(in addition to photochemical oxidation of isoprene)would cause the observed ratios of[MVK]/[isoprene]and[MACR]/[isoprene]to deviate from those calculated by the reaction yields of isoprene and OH(Grosjean et al.,2001).
| 图表编号 | XD0052051600 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.05.15 |
| 作者 | Zhenhao Ling、Zhuoran He、Zhe Wang、Min Shao、Xuemei Wang |
| 绘制单位 | School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University、Guangdong Province Key Laboratory for Climate Change and Natural Disaster Studies, Sun Yat-sen University、School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University、Guangdong Province Key Laboratory for C |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1–Reaction rate constants for isoprene, MVK and MACR (cm3/ (molecule.sec)”的人还看了
-

- 表2 在室温 (298 K) 下团簇Mn3BP各稳定构型转化过程的反应速率常数k和平衡常数K Tab.2 Reaction rate constants (k) and equilibrium constant (K) for change




![Table 3.Equations and regression coefficients for homogeneous and heterogeneous reaction kinetic models[28]](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/BJKY201901002_11900.gif)