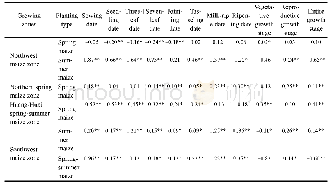
《Table 2 Changing trend of major phenological/growing stages length of maize in different regions fr
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《气候变化背景下1981-2010年中国玉米物候变化时空分异(英文)》
Note:”+”indicates the phenology/growing stages length delayed or prolonged;“”indicates the phenological/growing stages length advanced or shortened.**and*indicate significance levels at 0.01 or 0.05 respectively.
There was a significant inter-regional difference in the changes observed in maize phenological stages(Figure 3 and Table 2).Within the same zone,the phenological phases were significantly different for different maize planting types.In the northwest maize zone,spring maize showed an advancing trend from the sowing to the jointing date(0.05<θ<0.24d/yr),while the tasseling,milk-ripe,and ripening dates were delayed by 0.02,0.12,and 0.06d/yr;all phenological phases of summer maize,from sowing to ripening date,were delayed(0.21<θ<0.87 d/yr).All phenological phases of spring maize in the southwest maize zone were advanced(0.13<θ<0.53 d/yr).In contrast,the phenological phases of spring maize in northern China were mainly delayed(0.01<θ<0.30 d/yr),as only the seven-leaf stage was advanced(–0.14 d/yr).In the Huang-Huai spring-summer maize zone,the phenological phases of summer maize were delayed from the sowing to the ripening date(0.09<θ<0.35d/yr).The phenological phases of spring-summer maize were also delayed,and sowing data had a significant delay(0.96 d/yr);the sowing date of spring-summer maize was significantly delayed,resulting in the shortening of the entire growth stage.Due to the implementation of the intermittent growth system comprising spring maize,winter wheat,and summer maize in this zone,the sowing date of maize was affected not only by climate factors but also by the planting and harvesting time of the previous seasonal crop.
| 图表编号 | XD0047166900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.01 |
| 作者 | 刘玉洁、秦雅、葛全胜 |
| 绘制单位 | Key Laboratory of Land Surface Pattern and Simulation, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS、University of Chinese Academy of Sciences、Key Laboratory of Land Surface Pattern and Simulation, Institute of Geographic Sciences a |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2 Changing trend of major phenological/growing stages length of maize in different regions from 1981 to2010 (d/yr)”的人还看了
-
- Table 1 Trough values and trough separations of the opti-cal intensity changing with locations of the droplets
-
- Table 2 2016—2018 nurses’sociodemographic characteristics and trends of the agreement rates of defensive medical examina
-
- Table 2 2016—2018 nurses’sociodemographic characteristics and trends of the agreement rates of defensive medical examina
-
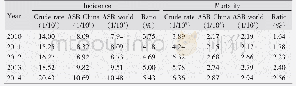
- Table 2 The trend of incidence and mortality of prostate cancer in Zhejiang cancer registration areas, 2010~2014





