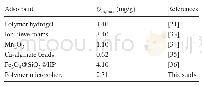
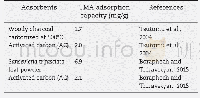
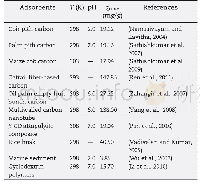
《Table 6–Comparison of 2, 4-DCP adsorption capacities of various adsorbents.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《One-step preparation of polyimide-inlaid amine-rich porous organic block copolymer for efficient removal of chlorophenols from aqueous solution》
The elemental compositions and mass content of the PI-bARPOP were analyzed by XPS,and the results are shown in Table 1.It was clear that the copolymers contained the elements C,N,and O,with C constituting the largest proportion.With the increase of PI content in the copolymer the weight percentage of O was gradually enhanced,while those of C and N were partly reduced.Especially for MA/TA/PMDA(4/2/2),the mass contents of C,N and O reached 44.69%26.13%and 29.18%,respectively.This was caused by the incorporation of anhydride groups from the PMDA monomer The XPS spectrum of MA/TA/PMDA(4/2/2)is shown in Fig.4From the survey scan(Fig.4a),it was obvious that three peaks were present which respectively corresponded to the elements C,N and O.According to the high-resolution C 1 s spectrum(Fig.4b),the four peaks at 284.6,285.4,286.9 and 288.0 eV could be attributed to the aromatic ring(–C=C–),linkage(–N–C–N–)triazine ring(–C=N–)and carbonyl group(–C=O),respectively implying that the monomers were sufficiently reacted(Yang et al.,2010,2017).In the high-resolution N 1 s scan(Fig.4c)the peaks at 398.0,398.7,399.4 and 400.0 eV,respectively corresponded to the triazine ring(–C=N–),amine group(–NH2)tertiary amine group(–N– (C)3) and imine group(–NH–)(Zhang et al.,2015) .In the high-resolution O 1 s pattern(Fig.4d),the peaks at 531.5 and 532.7 eV resulted from the carbonyl group(–C=O)and hydroxyl group(–OH),respectively(Kondo et al.2017).These results all indicated that the MA was successfully polymerized with TA and PMDA to form the novel PI-b-ARPOP copolymer.To further demonstrate the chemical structure of the block copolymer,MA/TA/PMDA(4/2/2)was analyzed by solid-state13C-NMR spectroscopy(Fig.5).It was clear that six resonances appeared in the spectra,which represented six carbon positions of the block copolymer.The resonance at166 ppm was assigned to the carbon atoms in the triazine ring of melamine.The 54 ppm resonance was derived from the tertiary carbon atoms,resulting from the primary amine groups of melamine reacting to form aminal groups.The resonance at 129 ppm originated from the–CH aromatic carbons in the benzene rings of TA(Schwab et al.,2009).The resonance of carbonyl carbons in the imide groups was observed at about 173 ppm.The resonance at 155 ppm belonged to the–CN3group in the triazine ring of melamine and the resonance of the aromatic carbons in benzene rings of PMDA was at 110 ppm(Chu et al.,2013).
| 图表编号 | XD0033526200 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.04.15 |
| 作者 | Yanyang Liu、Haijian Ou、Shangqing Li、Qingliang You、Huixian Liu、Guiying Liao、Dongsheng Wang |
| 绘制单位 | Engineering Research Center of Nano-Geomaterials of Ministry of Education,Faculty of Material Science and Chemistry,China University of Geosciences、Engineering Research Center of Nano-Geomaterials of Ministry of Education,Faculty of Material Science and C |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |