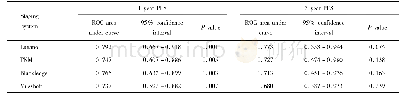
《Table 4 Comparison of image-guided systems in toric IOL alignment》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Image-guided lens extraction surgery: a systematic review》
NA:Not applicable.
It is well known that the three main factors that affect refractive performance in a toric IOL implantation are preoperative measurement,accurate alignment of the IOL and its stability in the bag[25].The accurate alignment of toric IOLs is crucial for the best possible postoperative refractive outcome and high patient satisfaction.However,for the best possible alignment,the consideration of the ocular cyclotorsion plays a pivotal role.A considerable number of studies were conducted in order to evaluate the accuracy of image-guided systems in toric IOL alignment and compare them with different conventional manual ink-marking techniques(Table 4).Among them,horizontal slit beam marking(HSBM)[34],subjective direct visual marking(SDVM)on the table(using a bevel knife tip)[34],marking with pendulum-attached marker[41]and withbubble marker instrument[26,28].For the assessment of imageguided systems in the alignment of toric IOLs,a variety of parameters were taken into consideration,including the mean toric IOL misalignment and rotation(the difference between the axis of the toric IOL 1h postoperatively and at consecutive follow-up timepoints)[26],the mean residual refractive cylinder,the mean uncorrected distance visual acuity(UDVA)as well as the BCDVA,the mean deviation from the target-induced astigmatism(TIA),and the mean overall time required for the alignment and for the whole cataract surgery.
| 图表编号 | XD0032750700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.18 |
| 作者 | Eirini-Kanella Panagiotopoulou、Panagiota Ntonti、Maria Gkika、Aristeidis Konstantinidis、Irfan Perente、Doukas Dardabounis、Konstantinos Ioannakis、Georgios Labiris |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Ophthalmology,University Hospital of Alexandroupolis、Department of Ophthalmology,University Hospital of Alexandroupolis、Department of Ophthalmology,University Hospital of Alexandroupolis、Department of Ophthalmology,University Hospital of Ale |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4 Comparison of image-guided systems in toric IOL alignment”的人还看了
-
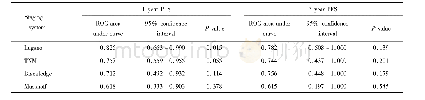
- Table 2.Comparison of 4 staging systems for predicting 1 year and 3 year PFS rates in PI-DLBCL patients according to ROC
![表1 Toric IOL规划表[35]](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/YRBH202101019_03800.gif)