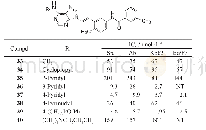
《Table 3 Area and proportion of NDVI varying grades》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《内蒙古植被NDVI变化趋势及影响因子数据集(2000–2015)》
The factor detection of geographic detector model was used to assess the influences of natural and human factors on the NDVI,expressed using q values.The core rationale of the factor detection module is that geographic phenomenon always exists in a certain place in space and is affected by environmental factors.If certain environmental factors change with geographic phenomenon in a remarkably consistent spatial pattern,then it indicates these environment factors have great effect on the occurrence and development of geographic phenomenon[7].Across the whole study area,the order of the degree of influence on NDVI was as follows:annual precipitation>soil type>vegetation type>grain yield>number of livestock>per capita net income of farmers and herdsmen>number of rural households>rural population>landform type>rural labor force>annual average temperature>slope>slope aspect.The first three factors are natural factors and the following two are human factors,which suggests that the influence of natural factors is greater than that of human factors.Similarly,for non-pastoral counties,the order was annual precipitation>soil type>vegetation type>grain yield>per capita net income of farmers and herdsmen>number of livestock>number of rural households>landform type>rural population>rural labor force>annual average temperature>slope>slope (Figure 3),again showing that natural factors had a greater impact.In contrast,the order for non-pastoral counties was grain output>rural labor force>annual average temperature>soil type>annual precipitation>number of rural households>per capita net income of farmers and herdsmen>number of livestock>total rural population>landform type>slope>vegetation type>slope aspect (Figure 3).These results indicate that human factors were dominant in such areas.
| 图表编号 | XD00206979600 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2020.06.25 |
| 作者 | 陈宽、潮洛濛 |
| 绘制单位 | 内蒙古大学生态与环境学院、内蒙古大学生态与环境学院 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 3 Area and proportion of NDVI varying grades”的人还看了
-
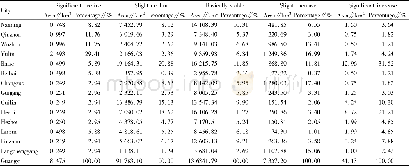
- Table 3 Area of different grades of vegetable NPP variations and percentage to the total area of Guangxi
-
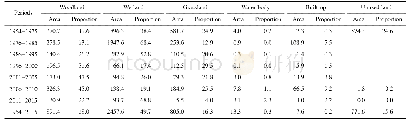
- Table 2 Area (km2) and proportions (%) of other land use converted to farmland of Baoqing County, Northeast China in dif
-
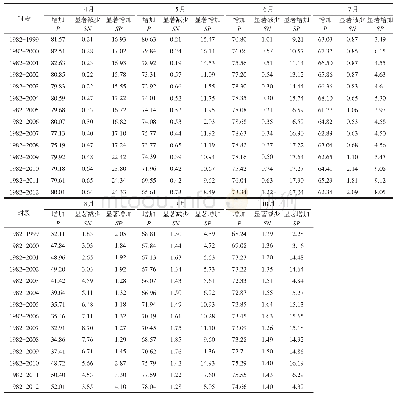
- 表6 月NDVI与气温正相关、显著负相关和显著正相关的区域面积比例Tab.6 Area proportions of different correlations between monthly NDVI and temperature