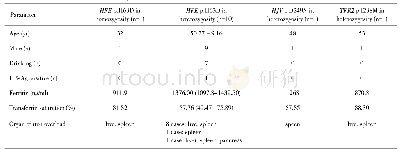
《Table 1 Main clinical features in patients with CF6and PCD7》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Chemoattractants and cytokines in primary ciliary dyskinesia and cystic fibrosis: key players in chronic respiratory diseases》
Abbreviations:ABPA,allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis;CF,cystic fibrosis;CFRD,CF-related diabetes;PCD,primary ciliary dyskinesia;SA,situs ambiguus;SI,situs inversus.
The coordinated movement of motile cilia on the lung epithelium is responsible for the upward transportation of lung mucus,wherein pathogens and harmful particles are captured.This process is called mucociliary clearance and is essential for keeping the lungs infection free.1Primary ciliary dyskinesia(PCD)and cystic fibrosis(CF)are both rare,autosomal-inherited disorders associated with impaired mucociliary clearance.2,3Although both diseases have a different genetic and functional origin,they share common features such as chronic respiratory infections characterized by excessive neutrophil influx.Indeed,high neutrophil counts and elevated neutrophil chemoattractant levels,for example,C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8/interleukin-8(CXCL8/IL-8),are present in the lungs of PCD and CF patients,even during stable conditions.4,5Despite the high neutrophil numbers and CXCL8/IL-8 levels,these patients suffer from persistent bacterial colonization and uncontrolled inflammation.3An overview of the most common clinical features in CF and PCD is listed in Table 1.
| 图表编号 | XD0010730300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.04.01 |
| 作者 | Maaike Cockx、Mieke Gouwy、Jo Van Damme、Sofie Struyf |
| 绘制单位 | Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Rega Institute for Medical Research, University of Leuven、Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Rega Institute for Medical Research, Un |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |