《Table 1Acidic properties of ZSM‐35 zeolites after sodium ion‐exchange treat‐ment.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《HZSM-35分子筛酸性质对甲缩醛和乙酸甲酯羟醛缩合反应的影响(英文)》
*Calculated through integration of IR peak.
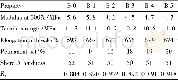
The IR characterization is used to clarify the change in the acidic properties of zeolites after the treatment.The intensity of the bridging OH groups at 3599 cm–1 suffers a significant de‐crease after sodium ion exchange,as illustrated in Fig.5(a),which indicates that the Br?nsted acidic proton of HZSM‐35zeolite is substituted by Na+.A higher exchange degree leads to a lower intensity of the Br?nsted acid hydroxyl groups.In HZSM‐35 zeolite,the IR band of Py H+appears at 1545 cm–1after adsorption of pyridine at 623 K for 30 min with the band of pyridine adsorbed on typical Lewis acid sites at 1445 cm–1(Fig.5 (b)) [41,42].The Lewis acid sites in HZSM‐35 are as‐signed to the extra‐framework aluminum species.The intensity of the band at 1545 cm–1 drops significantly with the pretreat‐ment of the sodium ion‐exchange process,which indicates a decrease in the concentration of Br?nsted acid in ZSM‐35 zeo‐lite.As shown in Table 1,the concentration of the Br?nsted acid in HZSM‐35 zeolite,obtained by the integration of the band at1545 cm–1,is 0.049 mmol/g,which decreases to 0.037 mmol/g in Na‐Z‐25 zeolite and even falls to 0.011 mmol/g in Na‐Z‐49zeolite.The concentration of the Lewis acid remains constant at0.004 mmol/g.
| 图表编号 | XD008199300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.11.01 |
| 作者 | 马占玲、马现刚、倪友明、刘红超、朱文良、郭新闻、刘中民 |
| 绘制单位 | 中国科学院大连化学物理研究所甲醇制烯烃国家工程实验室、大连理工大学化工与环境生命学部化工学院精细化工国家重点实验室、中国科学院大学、中国科学院大连化学物理研究所甲醇制烯烃国家工程实验室、中国科学院大连化学物理研究所甲醇制烯烃国家工程实验室、中国科学院大连化学物理研究所甲醇制烯烃国家工程实验室、中国科学院大连化学物理研究所甲醇制烯烃国家工程实验室、大连理工大学化工与环境生命学部化工学院精细化工国家重点实验室、中国科学院大连化学物理研究所甲醇制烯烃国家工程实验室 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |