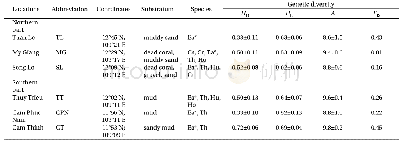
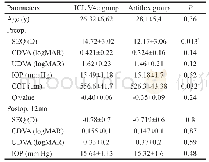
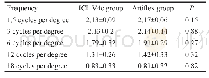
《Table 2 Ecological indicators in both sites, abundance (Aa, Ra) , dominance (Da, Rd) frequency (Fa,
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Eco-morphological characteristics of fern species for slope conservation》
The results obtained in this study showed a bigger diversity of vegetation species in the disturbed area(landslide scar)compared to the non-disturbed area(Table 2).These results matched the ones obtained on previous studies(Silvertown et al.1994;Grace 1999;Roberts 2004;Velazquez and Gomez-Sal 2009;Gonzalez-Ollauri and Mickovski 2017).In the study area,it was confirmed that ferns play an important role after disturbance quickly colonizing the slope but impeding other species to grow healthily,leading to decrease of species diversity over time.Previous studies on vegetation regeneration on landslide scars suggested similar results.For example:after four-year recovery from landslide in Panama,ferns were the common species colonizing the scar,shadowing woody colonizers(Garwood 1985);similarly,in the low montane forest of Puerto Rico(Guariguata 1990)and Nicaragua(Velazquez and Gomez-Sal 2009)ferns formed thick canopies on the landslide scar,and in the landslide scars of the upper montane forest in Jamaica,Gleichenia ferns are present as a rapid colonizer species after disturbance(Dalling and Tanner 1995).This can be related to the unique ecological features that a landslidepromotes,allowingsurrounding vegetation to colonize the affected slope,after topsoil and vegetation is driven downwards as suggested by Gonzalez-Ollauri and Mickovski(2017).
| 图表编号 | XD0056560600 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.01 |
| 作者 | Laura SANCHEZ-CASTILLO、Ken’ichirou KOSUGI、Naoya MASAOKA、Tetsuya KUBOTA |
| 绘制单位 | Faculty of Forestry Sciences,Autonomous University of Nuevo Leon、Forest and Biomaterials Science Division,Graduate School of Agriculture,Kyoto University、Forest and Biomaterials Science Division,Graduate School of Agriculture,Kyoto University、Forest Envir |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2 Ecological indicators in both sites, abundance (Aa, Ra) , dominance (Da, Rd) frequency (Fa, Rf) and importance v”的人还看了
-

- Table 2 Differentially expressed genes in the trans-regulatory networks existed in both GSE1420 and GSE26886 datasets