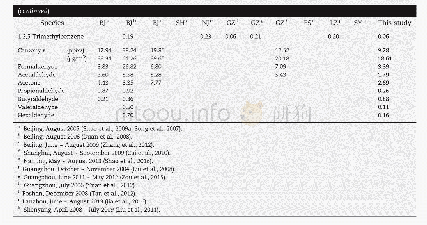
《Table 3–Performance comparison of GC–MS/MS with previously reported methods.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
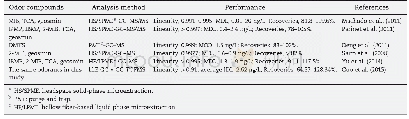
《Simultaneous quantification of fifty-one odor-causing compounds in drinking water using gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry》
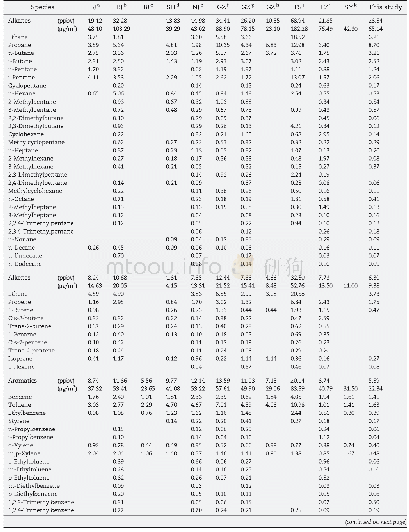
Using the developed LLE-GC-MS/MS method,the potential odorants of the intake and finished water from three DWTPs were determined.As indicated in Appendix A Table S3,a total of 19 odorants were detected in the three source waters and 10in finished waters,with concentration ranges of n.d.–1025.47and n.d.–128.33 ng/L,respectively.Furthermore,flavor profile analysis(FPA)was used to evaluate odor characteristics in water(Suffet et al.,1988),and the odor activity value(OAV)which was the ratio of the odorant concentration to the corresponding OTC(Appendix A Table S1),was used to assess the contribution of different odorants to the odor profile(Burdack-Freitag and Schieberle,2012).A compound with an OAV over 1 is considered to be important in constituting the odor profile.It was found that swampy/septic and musty/earthy odors were the major odor types for source water,with an odor intensity of n.d.–7.0 and n.d.–6.75,respectively,while no odor was detected in the finished water(Appendix A Table S3).The three DWTPs adopted an advanced treatment process combining ozone with biological activated carbon(ozone/BAC),which has been demonstrated to be effective for odor control in drinking water(Yang et al.,2010).As Fig.3 shows,for DWTP A and DWTP B,indole,DMTS,and DMDS were considered to be the key odorants responsible for the swampy/septic odor.Geosmin and 2-MIB were considered to be the key odorants related to the musty/earthy odor in DWTP B.The different odor profiles in the three DWTPs could be interpreted by the different raw water types,in which cyanobacteria were the main contributors of odor problems in lake and reservoir sources(Watson et al.,2008).The difference in the odorants'concentrations between DWTP A and DWTP B might be due to the fact that the water intake sites were different.It should be noted that the swampy/septic odor intensity was above 6 in DWTP A and B although the total OAVs of the detected thiothers and indole were low,illustrating the synergetic effects of other odorants on swampy/septic odor.
| 图表编号 | XD0052055200 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.05.15 |
| 作者 | Chunmiao Wang、Jianwei Yu、Qingyuan Guo、Yu Zhao、Nan Cao、Zhiyong Yu、Min Yang |
| 绘制单位 | Key Laboratory of Drinking Water Science and Technology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences、University of Chinese Academy of Sciences、Key Laboratory of Drinking Water Science and Technology, Research Center for Eco |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |