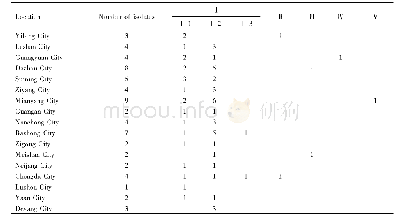
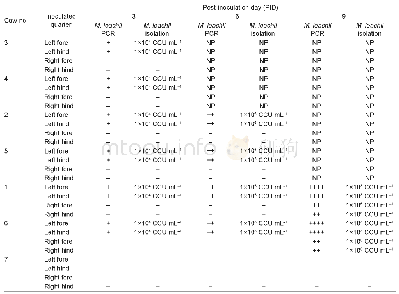
《Table 2 PCR detection and isolation of Mycoplasma leachii from milk samples of the inoculated cows》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Mycoplasma leachii causes bovine mastitis: Evidence from clinical symptoms,histopathology and immunohistochemistry"》
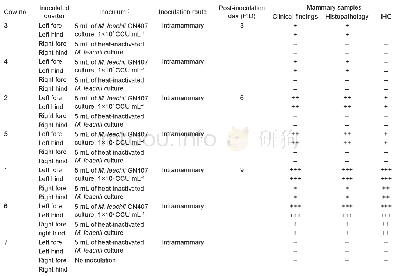
CCU,color changing unit;+,weakly positive in PCR detection;++,moderately positive in PCR detection;++++,strongly positive in PCRdetection;–,negative in PCR detection and M.leachii isolation;NP,these cows were euthanized,and the corresponding detect
The quarters of all M.leachii-inoculated cows were monitored for clinical manifestations throughout the experimental period.Histopathology and IHC detection of the mammary tissues were performed on PIDs 3,6 and 9.The clinical signs and histopathology of the M.leachii-inoculated quarters exhibited a gradual progression to severe mastitis over the 9-day experimental period(Table 1 and Fig.1),and the M.leachii antigen was detected by IHC in mammary tissue from the inoculated quarters of the affected cows on PIDs 6 and 9(Table 1 and Fig.2).The control quarters of the M.leachii-inoculated cows were histopathologically and immunohistochemically negative on PIDs 3 and 6,but they developed mild mastitis and histopathological changes on PID 9,and the M.leachii IHC signal was also detected in mammary gland epithelial cells of these control quarters(Table 1,Figs.1 and 2).Throughout the experimental period,however,the quarters of the negative control cow were clinically and histopathologically normal,and the M.leachii antigen was not detected in the mammary tissues of the control cow on PID 9(Table 1,Figs.1 and2).The clinical signs of the affected mammary glands were swelling and firmness,the produced milk was yellow and contained large ropy clots,and the milk yield of the inoculated quarters was markedly decreased compared to pre-inoculation.These results,particularly the detection of the M.leachii antigen in the mammary gland epithelial cells of the inoculated cows,indicated that the mammary gland lesions were directly caused by M.leachii.
| 图表编号 | XD0047427300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.20 |
| 作者 | CHANG Ji-tao、YU De-bin、LIANG Jian-bin、CHEN Jia、WANG Jian-fa、WANG Fang、JIANG Zhi-gang、HE Xi-jun、WU Rui、YU Li |
| 绘制单位 | Division of Livestock Infectious Diseases、State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Biotechnology,Harbin Veterinary Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences、College of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine,Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural Unive |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2 PCR detection and isolation of Mycoplasma leachii from milk samples of the inoculated cows”的人还看了
-
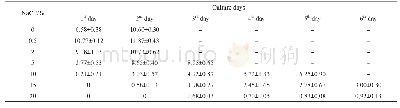
- Table 1 Growth of cultivable bacteria isolated from sediments in Tianjin Port in different salinities (×103 cfu/g)
-
- Table 1 Inoculation of lactating cows with passage cultures of Mycoplasma leachii strain GN407 via the intramammary rout