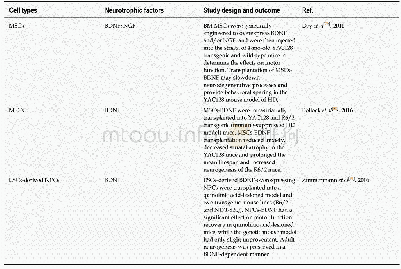
《Table 1 Transplantation of exogenous neural stem cells in the treatment of cerebral ischemia》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Exogenous neural stem cell transplantation for cerebral ischemia》
MCAO:Middle cerebral artery occlusion;VEGF:vascular endothelial growth factor;GABA:gamma-aminobutyric acid;(h)NSCs:(human)neural stem cells;HI:hypoxia-ischemia;d:day(s).
Transplantation of NSCs can enhance endogenous neurogenesis and is considered a promising strategy for the treatment of cerebral ischemia(Cheng et al.,2015;Bernstock et al.,2017).Preclinical studies have explored the feasibility of using NSCs to treat ischemic stroke,and have found that NSCs can survive and differentiate into neurons and astrocytes after transplantation,and that they can improve neurological recovery in rodent models of ischemia(Hou et al.,2017).Two clinical trials have shown that injecting NSCs from teratocarcinoma cell lines improved the European Stroke Scale motor score and the Everyday Memory test score of stroke patients;however,the sample size(4–7patients per group)was too small to demonstrate any therapeutic effects(Kondziolka et al.,2000,2005).Evidence from animal studies has shown that delayed transplantation of NSCs,at 3 days after cerebral ischemia,can have a neuroprotective role by inhibiting inflammation and focal glial scar formation,which suggests that NSCs may prolong the effective time window for the treatment of cerebral ischemia(Bacigaluppi et al.,2008).In a middle cerebral artery occlusion rat model,during acute ischemic injury(24 hours after ischemia),human embryonic NSCs that are directly transplanted into the infarcted cortical region using a microinjector can affect the proliferation of subventricular zone cells and the levels of angiogenesis in infarcted areas.Recent studies have also demonstrated that the intravenously transplanted human neural stem cell line HB1.F3 may provide neuroprotective effects in middle cerebral artery occlusion rat models by modulating early inflammatory events in cerebral ischemia(Watanabe et al.,2016).Thus,previous studies confirm that transplantation of NSCs could be an effective approach for treating cerebral ischemia.Recent reports of the transplantation of exogenous NSCs in treating cerebral ischemia are summarized in Table 1(Chen et al.,2014;Huang et al.,2014;Liu et al.,2014;Abeysinghe et al.,2015;Cheng et al.,2015;Rosenblum et al.,2015;Song et al.,2015;Yao et al.,2015;Bacigaluppi et al.,2016;Hou et al.,2017;Zhu et al.,2017).
| 图表编号 | XD0040617800 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.07.01 |
| 作者 | Ling-Yi Liao、Benson Wui-Man Lau、Dalinda Isabel Sánchez-Vidaa、Qiang Gao |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,West China Hospital,Sichuan University、Department of Rehabilitation Sciences,The Hong Kong Polytechnic University、Department of Rehabilitation Sciences,The Hong Kong Polytechnic University、Department of Rehabilitation |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1 Transplantation of exogenous neural stem cells in the treatment of cerebral ischemia”的人还看了
-

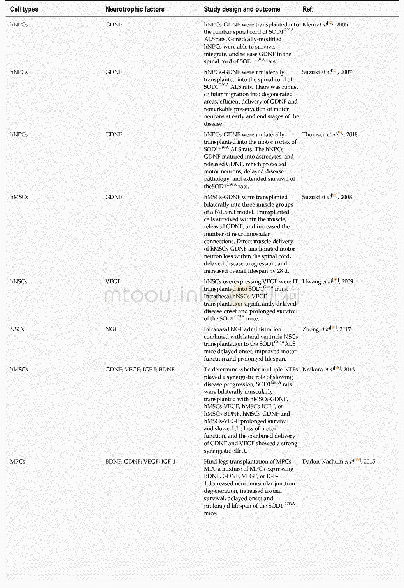
- Table 4 Combination therapy of stem cells with neurotrophic factors in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis