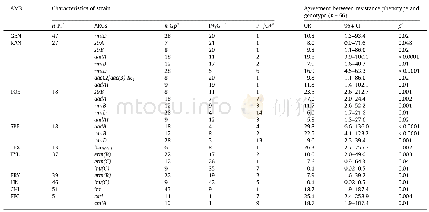
《Table 5 Associations of RE and AL with peripheral retinal changes》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
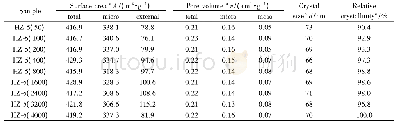
《Prevalence and characteristics of peripheral myopic retinopathy in Guangzhou office workers》
AL:Axial length;SE:Spherical equivalent;RE:Refractive error.aSignificance.
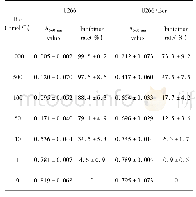
UCVA was markedly worse in the group with myopic retinopathy than in the remaining subjects(Table 4).The main reasons for this may be myopia-associated changes in the macula and the myopic RE-associated reduction in the size of the image on the retina.No gender difference was detected in the prevalence of myopic retinopathy in the present study,in agreement with the Beijing Eye Study[6],whereas Lai et al[17]reported a higher prevalence of myopic retinopathy in women.Our results also demonstrated strong associations between AL and SE and various retinal lesions.Overall,19.4%of the eyes with an AL of 25.34±1.56 mm,an SE of-4.02±2.92 D,and an optic nerve crescent of 0.38±0.34 had retinal lesions,whereas 80.6%of the eyes with an AL of 24.45 mm,SE of-2.09±2.42 D,and optic nerve crescent of 0.26±0.27 had no retinal lesions.This was consistent with previous studies by Jonas et al[25]and Pierro et al[26],who showed that eyes with posterior pole retinal changes,WWOP,paving stone degeneration,and lattice degeneration had significantly greater AL.After adjusted analysis for AL,our results also demonstrated that a higher magnitude of SE has an independent association with the presence of retinal lesions.Multivariate regression analysis identified moderate and high myopia as important risk factors for retinal lesions,suggesting that close follow-up of patients with moderate or higher myopia and with retinal changes might be warranted.Some studies have reported no significant association between myopic retinopathy and the level of education or rural versus urban regions of residence[27].Nevertheless,our study provides the first evidence that myopia is becoming more common among urban Chinese office workers,with a clear trend toward a higher prevalence of myopia in participants with a more recent birth year.Possible environmental reasons include an apparent increase in formal education and more time spent on near work tasks by East Asians[28-29].The subjects in our study had a higher level of education,as approximately 95%of them had a bachelor’s degree or above.Near work,such as reading and writing,may be a further factor associated with a higher prevalence of myopic retinopathy[30].The subjects were also urban,and the Beijing Eye Study reported that the urban population was significantly more myopic than the rural population[3],suggesting that urbanization may be associated with increased myopia.
| 图表编号 | XD0023065300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.08.18 |
| 作者 | Ting Zhang、Yan-Tao Wei、Wen-Bin Huang、Rong-Jiao Liu、Ya-Jing Zuo、Li-Wen He、Li-Ting Zhong、Shao-Chong Zhang |
| 绘制单位 | State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology,Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center,Sun Yat-Sen University、State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology,Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center,Sun Yat-Sen University、State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology,Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center,Sun Yat-Sen |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 5 Associations of RE and AL with peripheral retinal changes”的人还看了
-
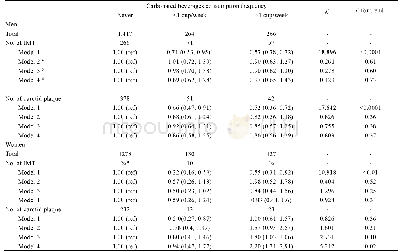
- Table 3 Associations between the frequency of carbonated beverages consumption and carotid atherosclerosis1
-
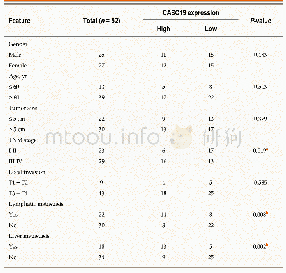
- Table 1 Associations of cancer susceptibility 19 expression with clinicopathologic features of patients with colorectal
-

- Table 1.Comparison of the peripheral blood percentage of Treg, Th17 and Th9 cells in peripheral blood of 2groups (±SD, %