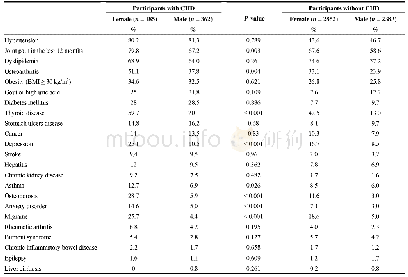
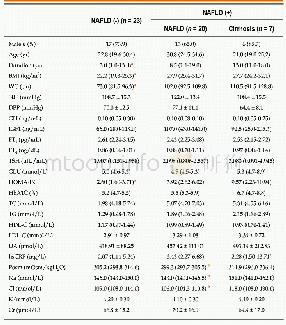
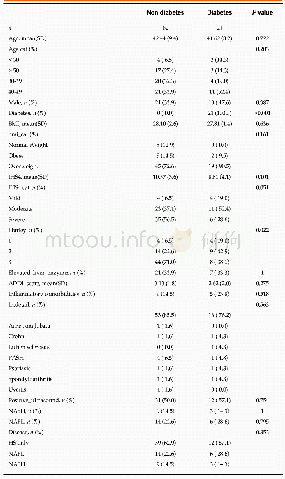
《Table 2Comparison of patients with and without postoperative complications.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Impact of postoperative intravenous fluid administration on complications following elective hepato-pancreato-biliary surgery》
Data are presented as median(interquartile range).
Complete data were collected on 241 patients(146 males;median age 63 years,range 19–84 years);their demographics are shown in Table 1.The median length of ICU stay was 1(range 1–54)days,whilst for total length of hospital stay this was 10(range3–154)days.The median(range)total intravenous fluid volume administered in the first 24 h postoperatively was 4380(10 0 0–11,585)mL of which 2200(200–3900)mL was crystalloid,1500(0–70 0 0)mL colloid and 680(0–3054)mL“other”fluid(primarily for the dilution of intravenous drugs)(Fig.1) .Thirty patients received a blood transfusion during the first 24 h in ICU,whilst fresh frozen plasma was given to three patients,platelets to one of those and additionally to two more.The median urine output in the first24 h was 1760 mL,surgical drain loss 200 mL and overall fluid balance+2857 mL(Fig.1).Central venous pressure(CVP)monitoring alone was used in 124 patients(51.5%),along with other readings of standard monitoring including heart rate and systolic and diastolic blood pressure.Mixed venous oxygen saturation(SVO 2)was used in addition to CVP in 107 patients(44.4%).LiDCO Rapid(LiDCO,London,UK)was used in 10 patients(4.1%)and parameters obtained included stroke volume,stroke volume variation,cardiac output and cardiac output index.Other parameters taken into consideration included age,cardiac and renal comorbidities as well as measured and ideal body weight.There were correlations between total intravenous fluid volume(r=0.278,P<0.001),positive fluid balance(r=0.344,P<0.001),intravenous colloid volume(r=0.278,P<0.001)and urine output(r=-0.295,P<0.001)with length of hospital stay.No correlation was seen between length of hospital stay and intravenous crystalloid volume.ASA grade was correlated to length of hospital stay(P<0.001),and also to volume of colloid received(P=0.009),total intravenous fluid received(P=0.011),urine output(P=0.025)and overall fluid balance(P=0.002).
| 图表编号 | XD0020452900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.10.15 |
| 作者 | Daniela Martin、Panagis M.Lykoudis、Gabriel Jones、David Highton、Alan Shaw、Sarahb James、Qiang Wei、Giuseppe Fusai |
| 绘制单位 | Division of Surgery & Interventional Science, University College London、Royal Free Perioperative Research Group, Royal Free Hospital、Division of Surgery & Interventional Science, University College London、Department of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Surgery & L |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2Comparison of patients with and without postoperative complications.”的人还看了
-

- Table 1 Difference significance of RNA absorbance of samples with and without liquid nitrogen grinding
-
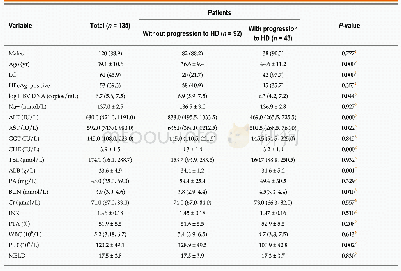
- Table 1 Baseline characteristics of patients with and without post-admission progression to hepatic decompensation
-
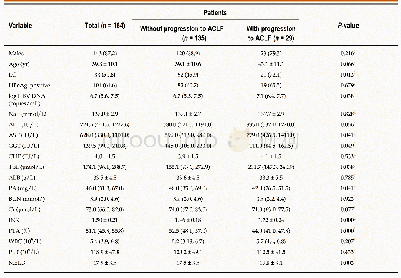
- Table 2 Baseline characteristics of patients with and without post-admission progression to acute-on-chronic liver failu