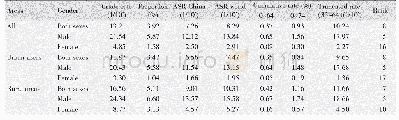
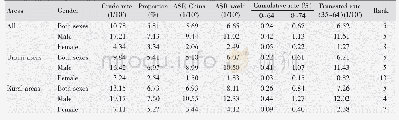
《Table 6 Chemokine GPCRs in cancer》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Chemokines in homeostasis and diseases》
Abbreviations:CCR,C-C cchemokine motif receptor;CXCR,C-X-C cchemokine motif receptor;GPCR,G-protein coupled receptor.
One of the epoch-making discoveries of chemokines and their GPCRs was the discovery of the ability of these molecules to mediate tumor cell chemotaxis,thus increasing the cell motility required for metastasis.This phenomenon was first reported for the chemokine MCP-1(CCL2),which mediates organspecific dissemination of experimental murine lymphoma,79,80an example of tumor cells utilizing the fundamental properties of chemokines for cell progression.This principle was later supported by evidence that chemokine GPCRs mediate metastasis of human tumor cells to distant organs.Since then,chemokines and their GPCRs have been shown to have a key role in the initiation and progression of cancers of multiple organs,including the lungs,colon,liver,breast,cervix,prostate,bladder,ovary,esophagus,skin and lymphatics.22,81–84Many cancer cells express chemokine GPCRs that sense ligands as growth signals and are the driving force for a motile phenotype that enables invasion and metastasis(Table 6).CXCR4 is one of the most frequently identified chemokine GPCRs in cancer and has been implicated in 423 human cancers,including breast,86–88ovary,89–91prostate,92,93pancreas,94–96melanoma,97,98esophagus,99lung,100head and neck,101bladder,102colorectum103and stomach cancers104as well as osteosarcoma,105neuroblastoma,106acutelymphoblastic leukemia85and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.107Activation oftheCXCR4–CXCL12axisiscorrelatedwith angiogenesis,90,120–124proliferation124–128and metastasis of tumors129–133(Table 7).CCR7 is another GPCR that has been frequently implicated in the progression of cancers113–118(Table 8),including breast,134melanoma,135,136lung,137head and neck,138colorectum,139chronic lymphocytic leukemia,140stomach,141non-Hodgkin’slymphoma142andT-cell leukemia.143Other chemokine GPCRs,such as CXCR3 in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia,85CXCR5 in head and neck cancer108and CCR2 in prostate cancer,lymphoma,glioblastoma,ovarian cancer and breast cancer109–112have been described.CCR9 and CCR10119were also implicated in cancer invasion and melanoma metastasis(Table 6).Notably,some cancers may exploit the function of more than one chemokine GPCR to their advantage,demonstrating thedelicate evasion of cancer cells from host defense.The bright spot,in this respect,is in the experimental system,as targeting chemokines or their GPCRs has shown beneficial effects on cancer therapy.
| 图表编号 | XD0010731000 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.04.01 |
| 作者 | Keqiang Chen、Zhiyao Bao、Peng Tang、Wanghua Gong、Teizo Yoshimura、Ji Ming Wang |
| 绘制单位 | Cancer and Inflammation Program, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute at Frederick、Cancer and Inflammation Program, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute at Frederick、Department of Pulmonary&Critical Care Medicine, Ruijin |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |