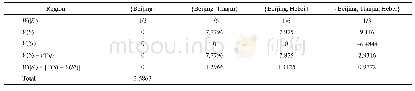
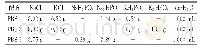
《Table 5 Distribution of species of Cd (%) ion in 0.01 mol L–1 NaNO3 at different pH values》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Removal of Cd and Pb with biochar made from dairy manure at low temperature》
p H value is one of the important parameters in the adsorption process,and affects metal ions competition for sorption sites in the natural environment.In addition,pH affects not only the surface charges of biochar,but also the speciation of the metal ions in solution.The pH values of BC300 and MBC were generally similar,with values of 9.75 and 9.98,respectively.Biochar derived from animal wastes such as poultry litter and cow manure typically has a higher ash content than that of biochar derived from lignocelluloses.Therefore,it has a higher pH value because alkalis,such as Na,K,Ca,and Mg,exist as oxides and carbonates in ash(Yuan et al.2011).Cd has little potential to hydrolyze when the pH is less than 7,and more than97%of Cd exists as Cd2+species in solution(Table 5).In comparison,hydrolysis of Pb is enhanced significantly when pH increases to 7.0,and only 76.71%of Pb exists in the form of Pb2+in solution(Table 6).Fig.3-A and B show the influence of pH on the competitive adsorption for Pb and Cd by BC.The initial pH of the solution has a strong effect on the adsorption capacity for Pb and Cd by BC,which increased with initial pH,especially for Pb.The adsorption efficiency of Pb and Cd was relatively low at low pH values because of the competitive adsorption between the hydronium ion and the metal ion in solution.
| 图表编号 | XD0047428200 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.20 |
| 作者 | CHEN Zhi-liang、ZHANG Jian-qiang、HUANG Ling、YUAN Zhi-hui、LI Zhao-jun、LIU Min-chao |
| 绘制单位 | Guangdong Engineering Technology Research Center of Heavy Metal Pollution Control and Restoration in Farmland Soil,South China Institute of Environmental Sciences、Guangdong Engineering Technology Research Center of Heavy Metal Pollution Control and Restor |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
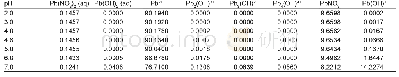
![Table 2 Distribution Coefficients of the recycled M[H]-11.9 lithium ion-sieve membrane](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/RGJT201903033_11400.gif)