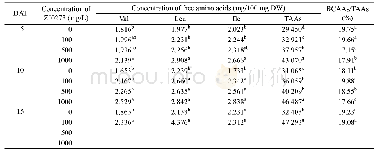
《Table 2 Effects of different concentrations of ZJ0273 on Fv/Fm, ФPSII, and NPQ in PSII at the fourt
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《除草剂丙酯草醚对大麦的影响和支链氨基酸对其生长的恢复作用(英文)》
Within a column,means at the same DAT followed by the same letters are not significantly different by the LSD test at P≤0.05 under completely randomized design.Data were analyzed separately at each measurement time.DAT:days after treatment;Fv/Fm:maximal
Increasing ZJ0237 rates of application significantly reduced maximal photochemical efficiency(Fv/Fm)of barley leaves at 1 DAT,and this reduction grew in the subsequent measurements(1–9 DAT;Table 2).The maximum reduction in Fv/Fm was observed in response to 1000 mg/L ZJ0273,which caused a 14.1%reduction(compared with controls)in Fv/Fm at 9 DAT.Changes in leafФPSII in response to ZJ0237 application followed a similar pattern to that of Fv/Fm.Although 100 mg/L ZJ0273 had no significant effect onФPSII at 1 DAT,a steep reduction inleafФPSII was recorded under 1000 mg/L ZJ0273 with increasing application period.For example,ФPSII was reduced by 13.6%at 1 DAT and by 46.4%at 9 DAT(compared with controls).In contrast to Fv/Fm,a significant increase in NPQ of barley leaves was observed in response to increasing the ZJ0237 application rate or the time after treatment,although the lower herbicide concentration(100 mg/L)had no significant effect on NPQ at 1 DAT.The 1000 mg/L ZJ0273 treatment increased NPQ by 72.8%at 1 DAT and by 124.4%at 9 DAT,compared with controls.No significant differences in the NPQ of the plants were detected between treatments of 500 or 1000 mg/L of ZJ0237 when measured at 5–9 DAT(Table 2).
| 图表编号 | XD0047004900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.03 |
| 作者 | Ling XU、Jian-yao SHOU、Rafaqat Ali GILL、Xiang GUO、Ullah NAJEEB、Wei-jun ZHOU |
| 绘制单位 | Zhejiang Key Lab of Plant Secondary Metabolism and Regulation and College of Life Sciences, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University、Zhuji Municipal Agro-Tech Extension Center、Institute of Crop Science and Zhejiang Key Lab of Crop Germplasm, Zhejiang University、Insti |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2 Effects of different concentrations of ZJ0273 on Fv/Fm, ФPSII, and NPQ in PSII at the fourth-leaf stage of barle”的人还看了
-
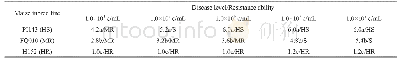
- Table 1 Effects of different concentrations of A.flavus conidial suspension on the disease level and resistance ability
-

- Table 3 Effects of different concentrations of GGR6 solutions on the rooting of semi-lignified cuttings
-

- Table 4 Effects of different concentrations of ZJ0273 on ALS and GST activity at the fourth-leaf stage of barley seedlin
-
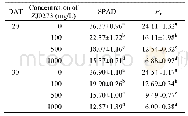
- Table 3 Effects of different concentrations of ZJ0273 on the SPAD value and Pn at the fourth-leaf stage of barley seedli