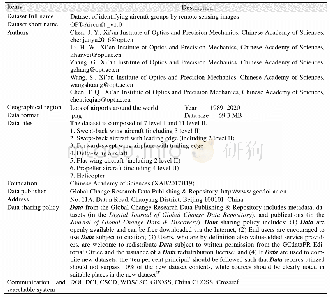
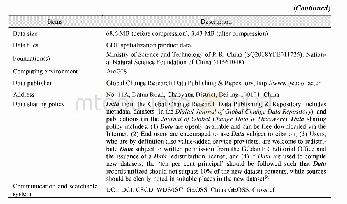
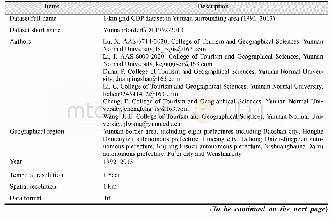
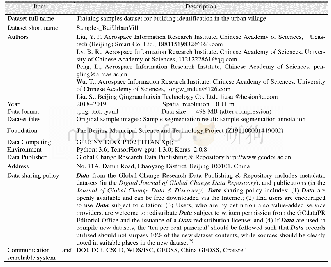
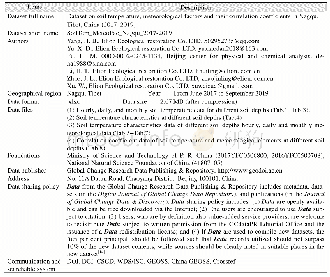
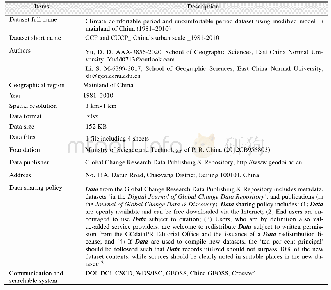
《Table 1 Metadata summary of the dataset》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《三江源及其毗邻地区公里网格降水数据集(2009–2013)》
According to the theory of precipitation in mountainous established by Fu[8],precipitation in a mountainous region is jointly determined by precipitation affected by macroscopic geographic factors and precipitation variation resulting from the difference in local elevation,and can thus be represented and calculated by a parabolic equation.The elevation difference of region is large,and precipitation in this area is greatly affected by the terrain,which satisfies the application condition of parabolic equation.In the studying region,the annual average precipitation is less than 1,000 mm,and precipitation has a positive correlation wtih NDVI in such region when excluding the effects of local topography.Therefore,the same function should fit the relationships between elevation and precipitation or NDVI.When not taking into consideration the effects of local topography,there is a positive correlation between precipitation and vegetation growth in sub-humid and semiarid regions,which can be represented by the linear response relationship between precipitation and NDVI[9-10].Hence,algorithm used in this study is to assume that both precipitation and NDVI are in a quadratic parabolic relationship with elevation.The parameters of the NDVI–DEM functionare first determined based on high-resolution NDVI and DEM data,then to estimate the parameters between DEM and precipitation.Finally,downscaled TRMM precipitation data was based on the high-resolution DEM data[3].
| 图表编号 | XD00206983700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2020.06.25 |
| 作者 | 蒋育昊、李宝林、袁烨城、高锡章、张涛、刘岩、李影、罗智勇、李红、马强、王晓敏、次仁多吉 |
| 绘制单位 | 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室、中国科学院大学、中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室、中国科学院大学、中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室、中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室、中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室、中国科学院大学、中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室、中国科学院大学、中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |