《Table 1.Changes in the energy budget, cloud fraction, and near-surface wind speed in the summer und
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Comparisons of urban-related warming for Shenzhen and Guangzhou》
The impacts of urban surface expansion on the SAT maximum and minimum in summer can be explained by changes in the energy budget during the daytime and nighttime(Table 1).Surface radiative forcings were all positive during the daytime,at 5.40 W m-2/12.33 W m-2over the entire area of Guangzhou/Shenzhen,and11.28 W m-2/28.99 W m-2over the urban areas.However,values were negative at nighttime(-1.58 W m-2/-1.86 W m-2over the entire area of Guangzhou/Shenzhen,and-4.69 W m-2/-2.71 W m-2over the urban areas).Precipitation increased during both daytime and nighttime over the entire area of the two cities and the urban areas,which was consistent with the increased cloud cover at different levels(with the exception of decreased low-cloud cover over the Guangzhou area at nighttime).The increased cloud cover further contributed to a weakened downward shortwave flux(daytime only)and an intensified downward longwave flux.Meanwhile,with the urban surface expansion,albedo decreased,which induced a weakened upward shortwave flux.This decreased downward shortwave flux(smaller)and increased upward shortwave flux(larger)induced a positive shortwave flux.
| 图表编号 | XD00187338400 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.07.16 |
| 作者 | ZHAO Deming、ZHA Jinlin、WU Jian |
| 绘制单位 | CAS Key Laboratory of Regional Climate-Environment for Temperate East Asia, Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences、Department of Atmospheric Science, Yunnan University、Department of Atmospheric Science, Yunnan University |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1.Changes in the energy budget, cloud fraction, and near-surface wind speed in the summer under EX1 and EX2 betwee”的人还看了
-

- Table 1 Photovoltaic parameters of the devices at the starting point in near space (35 km above the Earth)
-
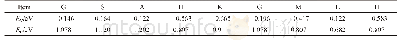
- Table 2 The energy value of EV and EC of Fe2Si bulk at the high-symmetry points in the Brillouin zone


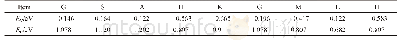

![Table 1 The viscosity activation energy of[Bmim][SCN]with different mass fraction of DCM](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/HGYJ201901022_09700.gif)