《Table 1:Distribution Effect of China’s Urban Personal Income Tax》
Source:Xu,Ma and Li,2013.
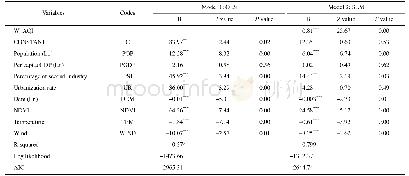
First,enhance the role of taxation in regulating income distribution.China’s current tax system has a limited effect in regulating income distribution.Tax structure,for instance,is tilted in favor of indirect tax such as VAT that contributes to increasing income gaps,while the share of direct tax such as personal income tax that helps narrow income gaps is too small(Nie,Yue;2012).Moreover,personal income tax is a salary tax imposed on salarymen and cannot regulate the income of people with other income sources.As Table 1 shows,personal income tax contributed more to narrowing income gaps between urban and rural residents since 2005 but the effect was limited.In 2009,personal income tax only reduced Gini coefficient between urban and rural residents by about one percentage point.It is necessary,therefore,to adjust tax structure by including taxes that help regulate income distribution:among them,property tax and inheritance tax are worth considering.Property tax will increase the share of direct tax and allow the government to conditionally exempt certain indirect taxes and invigorate enterprises.It will also effectively regulate the income of high-income groups.
| 图表编号 | XD007229800 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.07.08 |
| 作者 | 李实 |
| 绘制单位 | 北京师范大学收入分配研究院 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1:Distribution Effect of China’s Urban Personal Income Tax”的人还看了
-

- Table 1 The income on investment of the food industry in the three northeastern provinces of China and the entire countr
-
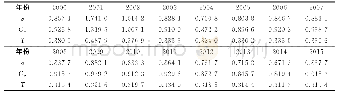
- 表1 2000-2015年黄河经济带县域城乡收入比的差异指数Tab.1 Theσ, Cv, T of urban-rural income ratio in Yellow River Economic Belt, 2000-2015
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式