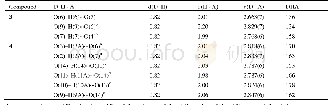
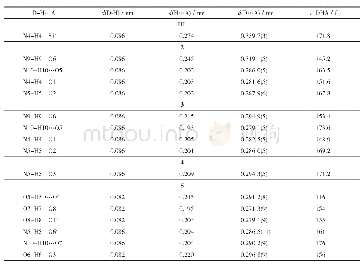
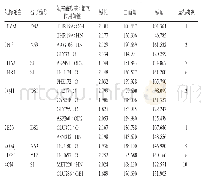
《Tab.3 Hydrogen bond date》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《丙二胺铜配合物的合成、晶体结构和热稳定性(英文)》
The thermal stability of the complex was quantitatively determined by TGA.The plots of weight loss and relative heat flow of the complex verse temperature are exhibited in Fig.3.The weight loss between 25℃and 164℃could be assigned to the escape of methanol from the complex,the weight loss 10.2%matched very well with the content of one molar CH3OH in the complex formula.The weight lose between 164℃and 230℃was corresponding to the dissociation of one pn,and the loss of the second pn happened in the range of 230-380℃,the relative weight losses were in agreement with the relative molecule's dissociation.From 380℃to 800℃,the weight loss could be attributed to the decomposition of CuCl2,where at 430℃,CuCl2 changed into CuCl,then it gradually decomposed into Cu and Cl2..The content of residual sample was 22.87%at 789℃,which was slightly larger than the content(20.19%)of Cu in the formula of the complex.According to theabove analysis,the thermal decomposition scheme for the complex can be proposed,and the scheme for the suggested procedure can be described as Scheme1.Differential scanning calorimetry has exhibited three endothermic reactions and two exothermic reactions.Methanol molecule produces a small sharp endothermic peak centered around 164℃,two pn molecules produce two endothermic peaks at 230℃and 330℃,respectively.And the decomposition of CuCl2 exhibits two exothermic peaks at 397℃and502℃,respectively.The results show that methanol molecule in lattice can be easily escaped from the complex because of its weak hydrogen bonding interactions with the other components in the complex.The decomposition of two pn molecules at higher temperature range indicates that pn has stronger coordination interactions with copper(II)ions.Cl-changed into Cl2 and escaped from the sample at temperature range from about 400℃to800℃,giving a strong support with the additional electrostatic interactions between Cu(II)and Clbesides their coordination interactions.
| 图表编号 | XD0043227000 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.01 |
| 作者 | 梅杰、田回香、夏语嫣、巫烨文、周红 |
| 绘制单位 | 武汉工程大学国际学院、武汉工程大学国际学院、武汉工程大学国际学院、武汉工程大学国际学院、武汉工程大学化学与环境工程学院 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |