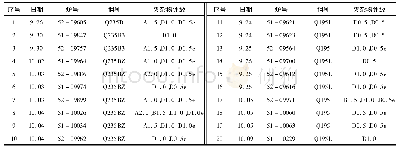
《Table 3.Major texture components observed in cold rolling of low-carbon steels》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Crystallographic texture and earing behavior analysis for different second cold reductions of double-reduction tinplate》
Some plots of the r-value versus angleαwith respect to the rolling direction are shown in Fig.11[15].Table 3shows the major texture components and their contribution to the drawability(rm)as well as to the tendency of earing(Δr)[15].The results in Fig.11 and Table 3 lead to some notable conclusions about desirable and undesirable orientations.For example,a strongγfiber texture or nearby component(i.e.,{554}<225>and{332}<113>)in low-carbon steels favors optimum deep drawability.The{554}<225>components increase with increasing degree of reduction,which is found to lead to values of rm=2.6 andΔr=1.1;this latter parameter indicates that this texture leads to the presence of 0 and 90°ears(Δr>0).By contrast,theαfiber textures,such as{113}<110>and{112}<110>,which have a negative value ofΔr,lead to the presence of 45°ears(Δr<0).In this case,controlling the relative intensity of these two kinds of components during rolling so as to attain nearly non-earing sheets is inevitable.Moreover,although the{100}<110>component possesses a relatively low value of absoluteΔr,which is beneficial for an excellent earing propensity,its poor rm value will undermine the deep drawability of sheets[16].
| 图表编号 | XD003088500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.06.01 |
| 作者 | Lu-hai Liao、Xiao-fei Zheng、Yong-lin Kang、Wei Liu、Yan Yan、Zhi-ying Mo |
| 绘制单位 | School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing、School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing、School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Tech |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |


![Table 2 Euler angles and Miller indices for common texture components in fcc metals and alloys[7]](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/WLGY201901028_12800.gif)