《Table 5 Evaluation of potential ecological risk in soils》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Analysis and Evaluation of Bioavailable Heavy Metals in Surface Soil of the Abandoned Lead-zinc Mine in Changhua,Hainan Province"》
Heavy metals are potentially harmful important pollutants.Heavy metals that enter the natural environment are not easily dissolved.They can enter the plants and animals through many natural and artificial pathways,and they may eventually enter and accumulate in the human body,and cause harm to human health.Therefore,it is necessary to classify the potential ecological risk degree of the toxicity coefficients of heavy metals quantitatively to carry out objective evaluation on the pollution status of heavy metals in soil.As shown in Table 5,the overall ecological risk indexes of heavy metals in the 3 study zones were in the order of Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn.In the tailing zone,the potential ecological risk index of Cd was 2 488.2,which exceeded the threshold of serious risk degree of 320,and the pollution degree reached the serious risk level;the potential ecological risk index of Pb was 151.95,and the pollution degree also reached the serious risk level;the potential risk indexes of Zn and Cu were less than 40,belonging to light pollution.In the reclaimed zone,the potential ecological risk index of Cd was 406.28,which exceeded the threshold of serious risk degree of 320,and the pollution degree reached the serious risk level;the potential ecological risk indexes Pb,Zn and Cu were all less than 40,and all were light pollution.In the peripheral zone,the potential ecological risk index of Cd was 2 218.85,which exceeded the threshold of serious risk degree of 320,and the pollution degree reached the serious risk level;the potential ecological risk index of Pb was 121.35,and the pollution was heavy,while the potential risk indexes of both Zn and Cu were less than40,belonging to light pollution.The contribution rates of the 4kinds of heavy metals in the 3 study zones to the compound ecological risk indexes were as follows:tailing zone(5.67%,0.18%,1.35%,92.80%),reclaimed zone(3.73%,0.46%,1.29%,94.52%),peripheral zone(5.47%,0.30%,1.7%,93.6%).The results showed that the potential ecological pollution of Pb was heavy in the abandoned lead-zinc mine,and the potential ecological pollution of Cd was serious.Moreover,the major contributors for ecological risk were Cd,Pb and Cu,in which the contribution rate of Cd was the largest,reaching 90%,so Cd was the main source of pollution.
| 图表编号 | XD00183078000 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.08.01 |
| 作者 | Jianping YUAN、Fangfang ZHENG、Dan WU、Tianhong YU、Qianqian JIANG |
| 绘制单位 | College of Geography and Environment,Hainan Normal University、College of Geography and Environment,Hainan Normal University、College of Geography and Environment,Hainan Normal University、College of Geography and Environment,Hainan Normal University、College |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 5 Evaluation of potential ecological risk in soils”的人还看了
-
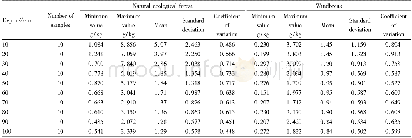
- Table 3 Analysis on variability of salt content in different soil layers with time (natural ecological forest and windbr
-
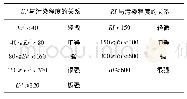
- 表2 单项及综合潜在生态风险评价指数与分级标准Tab.2 Individual and general indices and grades of potential ecological risk assessment
-

- 表5 Cfi、Eri和RI值对应的污染程度和潜在生态风险程度Tab.5 Degrees of pollution and potential ecological risk corresponding to the values of Cf





