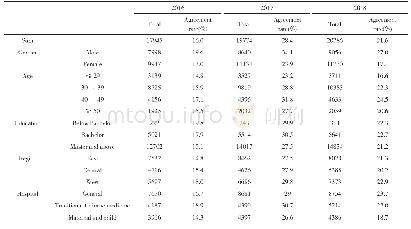
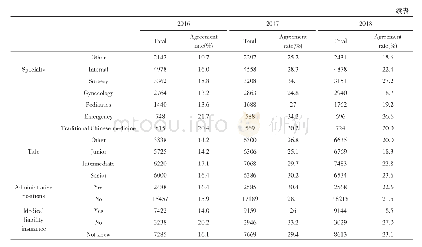
《Table 2 The time statistics of trend and multi-decadal wet and dry oscillation of regional mean ann
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Impact of oceans on climate change in drylands》
The drying of the drylands has resulted in a significant expansion of the global arid regions(Dai,2011a,2011b,2013a;Dai and Zhao,2017).Huang et al.(2016)analyzed the area change characteristics of the different climatic regions and found that most of the semi-arid regions showed an area expansion.Comparing the area of each semi-arid region in different time periods,it was found that the degree of aridification observed from 1990 to 2004 was more significant compared with the period from 1948 to 1962.The main reason for the expansion of aridification is the transition of humid and sub-humid regions to semi-arid regions,and the most significant aridification expansion occurred in East Asia,which contributed to almost 50%of the global aridification expansion(Figure 6).Fu and Ma(2008)pointed out that the east of Northwest China and the North China experienced significant interdecadal transitional changes from wet to dry in the 1970s,and these two regions and the southeastern part of Northeast China exhibited significant trend of aridification.In addition,the frequency of extreme droughts in the eastern part of Northwest China,North China and Northeast China has increased significantly since the1980s,with the largest increase being observed in Northeast China(Fu and Ma,2008).Li et al.(2015)studied the aridification of northern China and also found that the expansion of the semi-arid regions in China mainly occurred in the middle and lower Yellow River,Heilongjiang Province and the Gansu Province.
| 图表编号 | XD0034781200 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.06.01 |
| 作者 | Xiaodan GUAN、Jieru MA、Jianping HUANG、Ruixin HUANG、Lei ZHANG、Zhuguo MA |
| 绘制单位 | Key Laboratory for Semi-Arid Climate Change of the Ministry of Education, College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University、Key Laboratory for Semi-Arid Climate Change of the Ministry of Education, College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University、Key |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2 The time statistics of trend and multi-decadal wet and dry oscillation of regional mean annual precipitation in”的人还看了
-

- Table 3 Statistics of the trend in variation of autumn phenological time of five typical deciduous broad-leaved woody pl
-
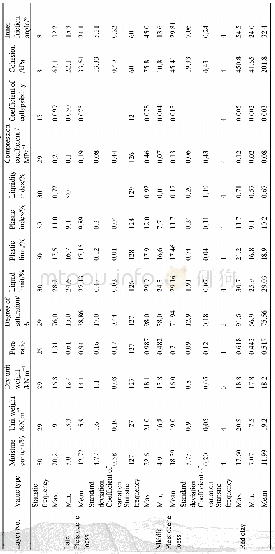
- Table 11 Statistics of Test Results of the Physical and Mechanical Indices of the Loess and Red Clay in Yan'an
-
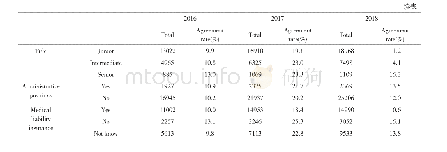
- Table 2 2016—2018 nurses’sociodemographic characteristics and trends of the agreement rates of defensive medical examina