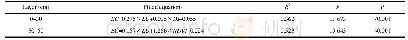《Table 3 Coefficients of multiple regression equations (b, b, b, b) and the related statisticsa)》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Impact of oceans on climate change in drylands》
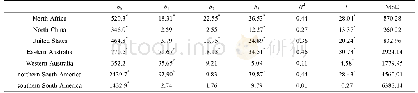
Huang et al.(2016)showed that the global drylands have been expanding over the past 60 years due to global warming.Dai et al.(2004)discovered that the global very dry areas have increased by more than twice since the 1970s,and global very wet areas have decreased,which is mainly related to the decrease of the precipitation and global warming caused by ENSO in the 1980s.However,in the latest research by Guan et al.(2017),it was reported that the longterm drought in the middle and high latitudes of the NH was alleviated during the warming slowdown period,mainly including the drylands in Eurasia and North America.This change was mainly measured using the AI.During the warming slowdown period,the temperature was still at a high level,and a change in the evaporation was not significant.However,the atmospheric circulation anomaly caused by the phase transition of the interdecadal index led to an increase in precipitation,and the AI also increased,as shown in Figure 10.Guan et al.(2017)further decomposed the AI into the dynamically induced AI(DAI)and the radiatively forced AI(RAI)using the dynamical adjustment method.The analysis found that the reversal of the AI is dominated by the slowdown of the decline of the DAI,and the slowdown of the DAI decline is also closely related to the phase changes of NAO,PDO and AMO.At the same time,Guan et al.(2017)also reported that,although the long-term drought in the middle and high latitudes of the NH was alleviated during the warming slowdown period,this was only temporary.Once the phase of the NAO,PDO and AMO changed,the world will change to a period of accelerated warming,and the existing slowdown period of drying will also disappear.
| 图表编号 | XD0034781100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.06.01 |
| 作者 | Xiaodan GUAN、Jieru MA、Jianping HUANG、Ruixin HUANG、Lei ZHANG、Zhuguo MA |
| 绘制单位 | Key Laboratory for Semi-Arid Climate Change of the Ministry of Education, College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University、Key Laboratory for Semi-Arid Climate Change of the Ministry of Education, College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University、Key |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 3 Coefficients of multiple regression equations (b, b, b, b) and the related statisticsa)”的人还看了
-
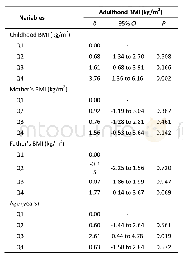
- Table 3.Multivariate Linear Regression Model to Evaluate the Effect of Childhood BMI and Parental BMI on Adulthood BMI (