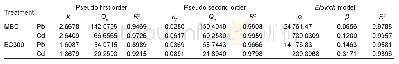
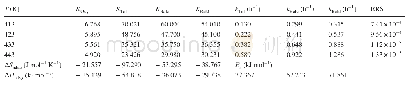
《Table 7 Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters in LH-OS-ND models》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Kinetics and Mechanism Modeling of Liquid-Phase Toluene Oxidation to Benzaldehyde Catalyzed by Mn–Mo Oxide》
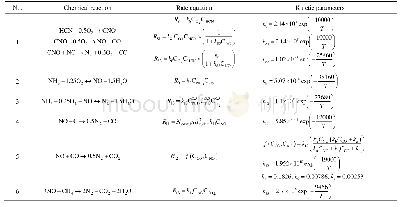
The initial conversion of toluene is much reduced at a low reaction temperature(413 K)with 2.0 g of catalyst,thus the concentrations of alcohol and aldehyde are considered trace amounts.Therefore,the terms c Balc and c Bald could be omitted in Eqs.(21)–(24).The left side of these equations should then be linear with toluene concentration.However,only the L–H competitive mechanism lacking the oxygen dissociation step seems to be rational.The others are not applicable as the intercepts of the fi tting lines of the models are negative,as shown in Table 6.Details of the L–H competitive nondissociative mechanism are depicted in Scheme 2,which was illuminated by Savara et al.[46].Undetermined parameters in the L–H model are calculated by applying the nonlinear leastsquares method.In addition,the thermodynamic changes in adsorption–desorption and the kinetic activation energies ofthe surface reactions are given in Eqs.(25)–(26).The distribution of the residual is uniform,and the residual sum of squares for the oxidation rate of toluene is below 1.50×10-3in the range of 413–443 K,as shown in Fig.S2.All evaluations of the proposed L–H mechanism are listed in Table 7.
| 图表编号 | XD0042636700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.01 |
| 作者 | Wang Li、Qingjun Zhang、Aiwu Zeng |
| 绘制单位 | School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University、School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University、School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 7 Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters in LH-OS-ND models”的人还看了
-
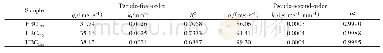
- Table 4 Adsorption kinetics parameters for Pseudo-first-order model and Pseudosecond-order model of Ni2+on HBCx