《Tab.1 Effects of catalyst, additive, and solvent on yielda》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"串联反应合成2-氨基-3,5-二氰基-4H-吡喃衍生物(英文)"》
aReactions were carried out using cyanochalcone(1a)(0.5mmol) ,malononitrile(2)(0.5 mmol) ,and base(0.05 mmol)in dichloromethane(5 m L)at 10℃for 20 h;bThe amount of additives:10 mol%(base);silica gel is 200~300 mesh.
Initially,we screened a variety of bases for catalysts as shown in Tab.1(Entries 1~13).Among the screened catalysts,inorganic bases showed superior catalytic activities when compared with organic bases.With the weak base sodium bicarbonate as the catalyst,the yield of the desired pyran product was 83.3%(Entry 1).The moderate base catalysts sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate afforded the products in 82%and 88%yields,respectively(Entries 2and 4).Although potassium hydroxide afforded product 3a in 97%yield(Entry 3),sodium hydroxide provided only a moderate yield of 72%(Entry 5).Turning to sodium acetate,the product 3a was obtained in89%yield(Entry 6).Finally,the weak base zinc acetate was proved to be the most efficient,affording the pyran product 3a in 98%yield(Entry 7).In comparison,organic bases showed overall lower catalytic abilities as DMAP and DABCO gave 68%(Entry 8)and61%(Entry 9)yields,respectively.Using zinc acetate as the catalyst,the effect of additives was also examined.Among the additives we tested(Entries 10~13),none of them was shown to further improve reaction efficiency according to the corresponding yields.For this reason,additives were not employed in the reaction optimization process.
| 图表编号 | XD0038116600 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.01 |
| 作者 | 尹晓刚、吴小云、付海、班大明、陈卓、龚维 |
| 绘制单位 | 贵州师范大学化学与材料科学学院、贵州省功能材料化学重点实验室、贵州师范大学化学与材料科学学院、贵州省功能材料化学重点实验室、贵州省功能材料化学重点实验室、贵州师范大学化学与材料科学学院、贵州省功能材料化学重点实验室、贵州师范大学化学与材料科学学院、贵州省功能材料化学重点实验室、贵州省功能材料化学重点实验室 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Tab.1 Effects of catalyst, additive, and solvent on yielda”的人还看了
-

- 表2 膦配体和催化剂对化合物Ⅰ分离收率的影响Tab.2 Effects of phosphine ligands and catalysts on separation yield of compoundⅠ
-
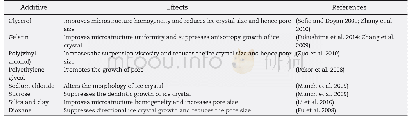
- Table 2–Types of additives used in ice-templating and their respective effects on microstructure evolution.





