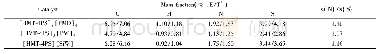
《Table 3 Elemental composition of bimetallic catalysts by XRF analysis》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Preferential Surface Decoration of Supported Co Catalysts with Pt for Aromatic Saturation》
During the synthesis of Pt-Co/Si O2-GR,the driving force for the galvanic replacement reaction comes from the difference in reduction potentials(1.18 V for the Pt2+/Pt pair and-0.28 V for the Co2+/Co pair)[23].When the reduced Co/Si O2 was added to the Pt2+solution,it was assumed that a galvanic replacement reaction occurred between Pt2+and Co,leading to the preferential deposition of Pt on the surfaces of Co nanoparticles instead of Si O2 support.Thereby,we have performed the ICP-AES analysis of the supernatants during the galvanic replacement reaction to verify the above assumption(Table 2).Only a trace amount of Pt2+ions(2.5%)could be removed by washing after the galvanic replacement reaction for Pt-Co/Si O2-GR,but obviously Pt2+ions(82%)could be removed by washing the control samples,which were subjected to the identical synthesis process of galvanic replacement except the process for reduction of Co.This fact indicated that the Pt located onto the catalysts existed in the state of metallic Pt,which could not be removed by washing;while that Pt in the control samples existed in the state of adsorbed Pt2+ions,most of which would be washed away after being dissolved in water.The comparing experiments of ICP-AES revealed that most of Pt was preferentially decorated onto the surface of Co instead of the support.Moreover,the XRF analysis of the solid catalysts suggested that the elemental compostion of Pt-Co/Si O2-GR was identical to that of Pt-Co/Si O2-CI(Table 3).
| 图表编号 | XD0011292500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.03.30 |
| 作者 | Zheng Renyang、Zheng Peng、Dong Xiao、Zheng Aiguo、Li Huifeng、Li Mingfeng |
| 绘制单位 | Research Institute of Petroleum Processing (RIPP),SINOPEC、Research Institute of Petroleum Processing (RIPP),SINOPEC、Innovative Catalysis Program, Key Lab of Organic Optoelectronics and Molecular Engineering, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University、Re |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |