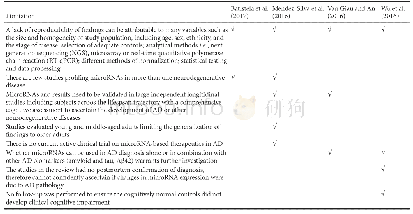
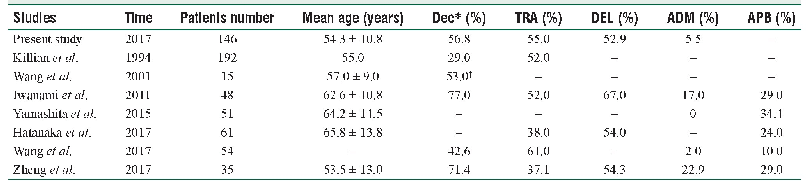《Table 1 Limitations of previous studies of microRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) as indicated in fo
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《MicroRNAs as diagnostic and therapeutic tools for Alzheimer's disease: advances and limitations》
√indicates that the parameter was mentioned as a limitation in the review article.Aβ:β-Amyloid peptide.
Increasing evidence suggests that microRNAs are dysregulated in neurodegenerative diseases such as AD,Parkinson’s disease,and stroke.Circulating microRNAs within blood may be characterized and used as minimally invasive diagnostic biomarkers.They may facilitate the early detection of the disease and potentially the continual monitoring of disease progression and allow therapeutic interventions to be evaluated.Four recent reviews have been published on studies of microRNAs in AD.They were by Batistela et al.(2017),Mendez-Silva et al.(2016),Van Giau and An(2016),Wu et al.(2016)and,where reported,included studies up to June 2015 and September 2015.Each of the reviews identified areas of weakness or limitations in the reported studies(Table1)and the findings were often conflicting.The limitations included small size and heterogeneity of study populations,no postmortem confirmation of AD diagnosis or assay of other biomarkers,variations in analytical methods and platforms used and validation of findings,different methods of normalization,statistical testing and data processing,selection of cognitively normal controls(NC)and no confirmation that they did not develop clinical cognitive impairment.Also Ren et al.(2016)indicated that in many of the previous studies on microRNAs in brain,CSF,and blood from AD patients,most samples were from patients being treated with acetylcholinesterase inhibitor,which could have a confounding effect on analysis,rather than de novo drug-na?ve patients.Interestingly,differential correlation analysis using paired microRNAs detected different and more sensitive plasma microRNA biomarkers for MCI than were found by single molecule analysis using a t-test(Kayano et al.,2016).Plasma paired microRNA sets were shown to have high sensitivity and specificity for differentiating MCI from age-matched control,and also differentiated AD from age-matched control.In addition,the paired microRNA sets detected MCI in 7 of 10 elderly patients at asymptomatic stage 0.5–5 years preceding the clinical diagnosis(Sheinerman et al.,2012).
| 图表编号 | XD0040607700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.01 |
| 作者 | Bridget Martinez、Philip V.Peplow |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Physics and Engineering, Los Alamos National Laboratory、Department of Anatomy, University of Otago |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |