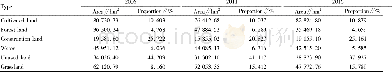
《Table 1–Properties and classification of seven antibiotics detected.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Distribution and relationship between antimicrobial resistance genes and heavy metals in surface sediments of Taihu Lake,China"》
The concentrations of antibiotics in the surface sediment of Lake Taihu are represented in Fig.2.A total of 7 out of the 14target antibiotics were detected in the seven sediment samples(their properties are represented in Table 1).However,sulfamethoxazole,sulfamethizole,erythromycin,roxithromycin,chloramphenicol,thiamphenicol,and florfenicol were not detected in any of the seven sediment samples.In the surface sediments,concentrations of∑TCs including tetracycline,oxytetracycline doxycycline and aureomycin,∑SAs including sulfadiazine and∑QNs comprising norfloxacin and ofloxacin ranged from 0.01 to 0.96,0.03 to 0.10 and 2.42 to 12.93 ng/g,respectively.The mean concentration levels of antibiotics in the surficial sediment of Taihu Lake were,0.05,9.05,2.59,0.09,0.53,0.44 and 0.583 ng/g representing sulfadiazine,norfloxacin,ofloxacin,doxycycline,tetracycline,oxytetracycline and aureomycin,respectively(Table 2).The most abundant antibiotics were norfloxacin and tetracycline,which was found at all the sampling sites except site S7(Yixing coastal zone).Site S4(Southwest zone)recorded the highest abundance of norfloxacin.Ofloxacin was the next most abundant antibiotic.It was present in S1(Tuoshan),S2(Manshan)and S3(Central zone).Only norfloxacin and tetracycline were found in S1-S6.There were no antibiotics found at site S7(Yixing Coastal zone).
| 图表编号 | XD0033522100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.15 |
| 作者 | Okugbe E.Ohore、Felix Gyawu Addo、Songhe Zhang、Nini Han、Kwaku Anim-Larbi |
| 绘制单位 | Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Integrated Regulation and Resource Development on Shallow Lakes, College of Environment, Hohai University、Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Integrated Regulation and Resource Development on Shallow Lakes, Coll |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1–Properties and classification of seven antibiotics detected.”的人还看了
-

- Table 1 Classification of Brassica campestris L.germplasm resources and statistics of protein and oil content
-
- Table 1.Effects of gradual soil drying on soil and plant analyzer development(SPAD)value of seven rice genotypes at diff