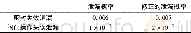《Table 2Efficacy of revision for occluded bilateral SIS placement.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Revision of bilateral self-expandable metallic stents placed using the stent-in-stent technique for malignant hilar biliary obstruction》
SIS:stent-in-stent;ERCP:endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography;SEMS:self-expandable metallic stent.
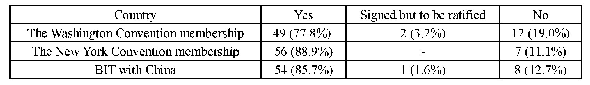
Endoscopic revision was initially attempted for all study subjects with occluded bilateral SIS placement.Technical success rate for endoscopic revision was 76.3%(29/38)(Table 2) .Endoscopic revision was failed due to tight biliary stricture in six patients,duodenal obstruction in 2 patients,and instability during ERCP in 1patient.Unilateral and bilateral plastic stent placements were carried out in 12 and 7 patients,respectively.Unilateral and bilateral additional SEMS placements were performed in 5 and 1 patients,respectively.Four patients underwent only cleaning of the occluded bilateral SIS placement.Clinical success for revision was achieved in 15(51.7%)patients,and the mean patency of revision was 49.1 days.Seventeen patients underwent secondary revision.Among the 14 patients who did not achieve the clinical success for revision,9 underwent percutaneous biliary drainage,2 underwentsecondary endoscopic revision,and 3 died.Univariate analysis revealed no significant predictive factors for clinical failure of revision(Table 3).The mean patency of revision was 37.0 days with plastic stent and 39.0 days with SEMS respectively and there was no statistically significant difference(P=0.917).
| 图表编号 | XD0020453900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.10.15 |
| 作者 | Junc Hyuk Son、Hee Seung Lee、Sang Hyub Lee、Seungmin Bang、Jinwoo Kang、Woo Hyun Paik、Ji Kon Ryu、Yong-Tae Kim |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Internal Medicine and Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine、Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital、Department of Internal Medicine, Institute |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |