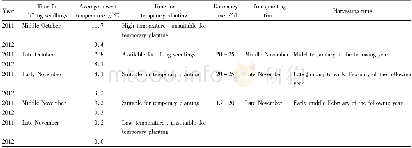
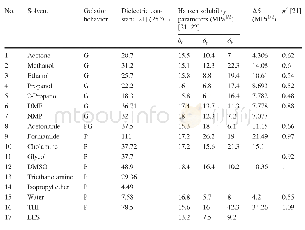
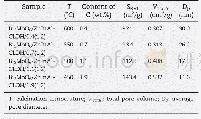
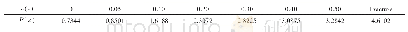《Table 1–Determination of surface porosity parameters for different plain PLGA formulae.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Novel technique of insulin loading into porous carriers for oral delivery》
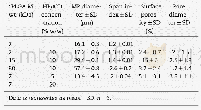
The effect of PLGA Mwt on surface porosity was also examined using three different Mwts(7,15,80 KDa)of the polymer.By visual inspection and surface porosity data(Table 1),it can be noticed that surface and bulk pores significantly increased from 2.4%±0.7%to 15.4%±6%(P<0.001),with increasing Mwt from 7 to 15 k Da but by further increase in Mwt,MP porosity decreased again to 2.8%±2.3%.This may be due to the fact that the higher the Mwt of PLGA,the faster the polymer precipitation forming solid polymer-shell during MP premature stages.Consequently,porogen premature escape will be minimal as the polymer precipitates and the porogen can be held within the polymer matrix,afterward,porogen extraction to the external aqueous phase can be achieved and the MPs will be more porous due to the defects produced during the escape of porogen through the formed viscous shell[30].However,with further increase in Mwt from 15 to 80 k Da the polymer solution becomes too viscous for the porogen to be extracted in the external water phase leading to the formation of MPs with lower porosity[29].In all formulations both pore diameters and pore diameter distribution were not significantly affected by either PLGA Mwt or HPβCD concentration but rather the density of surface pores was significantly affected by both parameters.It is also clear that increasing the polymer Mwt had a direct relation to MP size and span index(P<0.001);reaching up to 40±20μm with the highest PLGA Mwt.From the data above,we used HPβCD concentration of10%(w/w)and polymer Mwt of 15 k Da for further investigations.
| 图表编号 | XD00186267400 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.07.01 |
| 作者 | Sarah Y.Eilleia、Mahmoud E.Soliman、Samar Mansour、Ahmed.S.Geneidi |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Pharmaceutics and Industrial Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy,Ain Shams University、Department of Pharmaceutics and Industrial Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy,Ain Shams University、Department of Pharmaceutics and Industrial Pharmacy, Faculty of Pha |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1–Determination of surface porosity parameters for different plain PLGA formulae.”的人还看了
-

- Table 4–The effect of selected CS molecular weight and concentration on surface porosity%for plain PLGA MPs using double