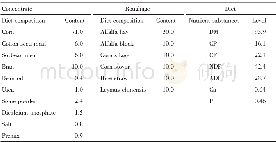
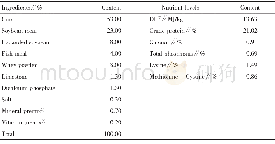
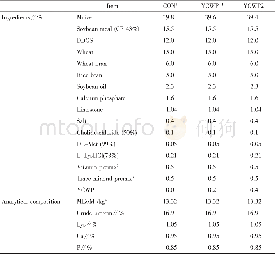
《Tab.1 Diet composition (as-fed basis)》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Effects of Dietary Yeast Cell Wall Polysaccharides Supplementation to Late Gestation and Lactation Diets on Reproductive Performance and Blood Profiles of Sows and Their Offspring》
Note:1.CON,basal diet;YCWP1,(CON+0.2%YCWP) ;YCWP2,(CON+0.4%YCWP) .2.Provided per kilogram of diet:niacin,55.07 mg;pantothenic acid,33.04 mg;vitamin A,11 013 IU;vitamin D,2 753IU;vitamin E,55 IU;riboflavin,9.9 mg;vitamin K,4.41 mg;vitamin B12,0.0
A total of 96 sows(Landrace×Yorkshire)were randomly allotted to three treatments based on breed,parity(2-3)and their respective d 85 of gestation.Dietary treatments consisted of CON(basal diet,treatment 1),YCWP1(CON+0.2%YCWP,treatment 2)and YCWP2(CON+0.4%YCWP,treatment 3).YCWP was incorporated into the YCWP diets via corn substitution.During gestation,sows were housed in individual gestation crates(0.6 m×2.0 m).Each crate was equipped with a stainless steel nipple for water.Sows were fed lactation diets and the feed intake during the gestational treatment was restricted(3.0 kg of feed daily).Then,sows were transferred to farrowing crates(2.13 m×0.66 m)and were fed separately from d 108 of gestation until weaning.From d 108 to d 111 of gestation,the diet was provided for ad libitum consumption.Around farrowing,all sows received 2.0 kg of feed daily,which was followed by2.0-3.0 kg of feed on d 2-3 post-farrowing.Thereafter,this amount was increased daily by 1.0 kg until ad libitum feeding.Sows had ad libitum access to water.Each crate had steel mesh floors with a heat lamp for newborn pigs.The farrowing room temperature was maintained at approximately 18 to 20℃.Rooms were mechanically ventilated.All experimental diets(Tab.1)were formulated to be isonitrogenous and isocaloric according to NRC[17].
| 图表编号 | XD00183466300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.02.01 |
| 作者 | Wang Yachao、Li Yuanfeng、Ao Xiang、He Jian |
| 绘制单位 | College of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology、College of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology、Swine Research Institute,Tie Qi Li Shi Group.Co.、College of Life Science and En |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |